What is Eosinophilic Esophagitis?
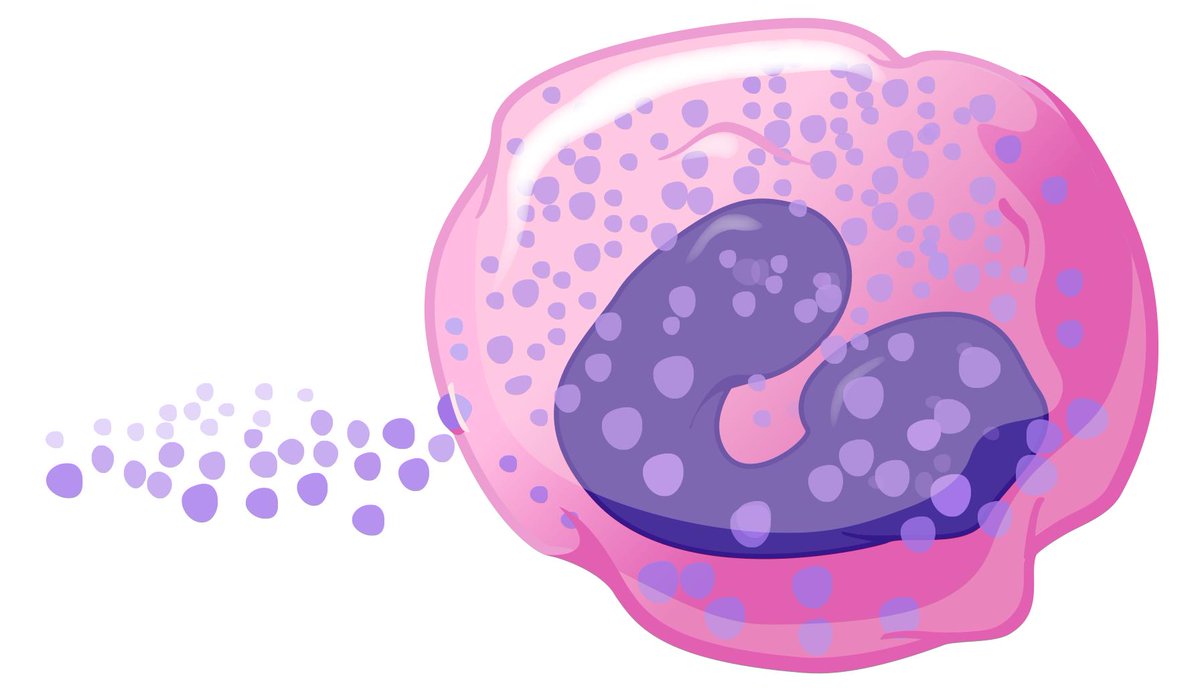
Eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE) is a chronic inflammatory disease of the esophagus. It is characterized by elevated levels of eosinophils (a type of white blood cell) in the esophagus. The accumulation of eosinophils causes inflammation and damage to the esophagus. Symptoms usually include difficulty swallowing, abdominal pain, vomiting, dysphagia, heartburn and food impaction.
Causes of Eosinophilic Esophagitis
The exact cause of EoE is unknown, but it is considered an immune-mediated disease. Factors that may contribute to its development include genetics, allergies and environmental factors. Research suggests people with EoE have a hypersensitivity to certain foods, particularly wheat, milk, soy, eggs and nuts. Exposure to these foods triggers an inappropriate immune response that causes eosinophils to accumulate in the esophagus and cause inflammation. Other potential causes include infections, medications, food additives and pollen or airborne allergens. More research is still needed to fully understand what triggers the disease.
Symptoms of Eosinophilic Esophagitis
Common symptoms of EoE include:
– Difficulty swallowing (dysphagia) – This is the most common symptom of Eosinophilic Esophagitis. It may affect both solids and liquids.
– Food impaction – Difficulty swallowing can lead to feelings of food becoming stuck in the throat or chest. This occurs when a bolus of food lodges itself in the swollen esophagus.
– Chest pain – Pain often occurs when swallowing and may radiate to the back.
– Heartburn – The inflammation caused by EoE can mimic the symptoms of acid reflux.
– Vomiting – This sometimes occurs after eating due to difficulty swallowing.
– Abdominal pain – Pain in the upper abdomen between or after meals.
– Failure to thrive in children – Children may not want to eat due to symptoms which can impact weight gain and growth.
Diagnosing Eosinophilic Esophagitis
There is no single test to diagnose EoE, but doctors use a combination of methods:
– Medical history and symptoms – A thorough history helps determine if symptoms suggest EoE.
– Physical exam – The doctor examines for signs of dehydration, food impaction or malnutrition.
– Endoscopy – A lighted, flexible tube is inserted down the throat to visually examine the esophagus for signs of inflammation or narrowing. Small biopsy samples are also taken.
– Pathology – Biopsies are analyzed under a microscope by a pathologist to identify eosinophil counts higher than normal in the esophagus. Counts greater than 15 eosinophils in a high power field are considered diagnostic of EoE.
– Other testing – Additional tests like a barium swallow x-ray or PH probe may help determine severity and rule out other conditions. Bloodwork usually shows no abnormalities.
Treatment of Eosinophilic Esophagitis
Currently there is no cure for EoE, but various treatments provide effective management of symptoms:
– Diet therapy – Eliminating specific food triggers through an elimination diet is often the first-line treatment.
– Medications – Topical corticosteroids are usually prescribed to reduce inflammation. Short-term swallowed steroids can help manage flare-ups.
– Dilatation – To widen a strictured esophagus using bougie dilators or balloons if symptoms persist despite other treatments.
– Surgery – Rarely needed and reserved for patients with complications like a perforation or debilitating pain.
Outlook for Eosinophilic Esophagitis
With proper treatment and diet management, many patients find relief from their EoE symptoms. Adherence to treatment is important to avoid scarring and narrowing of the esophagus over time. However, continuing problems relating to food triggers may require lifelong care. With an established diagnosis and well-managed dietary modifications, a good quality of life is possible with EoE. Current research efforts continue working towards improved treatments and understanding its causes. Prompt diagnosis leads to the best outlook for preventing progressive damage to the esophagus. With support, patients can learn to cope well with EoE as a chronic condition.
Living with Eosinophilic Esophagitis
A diagnosis of EoE brings many changes to daily routines and eating habits. The good news is that with diligent care, exacerbations can usually be prevented. Following the prescribed treatment plan and making healthy lifestyle adjustments can empower better management of the disease. It is important not to feel alone and connect with others living with EoE through patient support groups. Counseling can help address normal emotional reactions to a chronic illness as well. Focusing on health instead of specific food restrictions promotes overall well-being. With open communication between patients and providers, tailored diets can satisfy dietary needs and maintain quality of life. Over time, mindfulness of triggers helps build confidence around enjoyable eating. Taking EoE seriously today supports a sustainable future of disease control and reduced symptoms.
*Note:
1. Source: Coherent Market Insights, Public sources, Desk research
2. We have leveraged AI tools to mine information and compile it