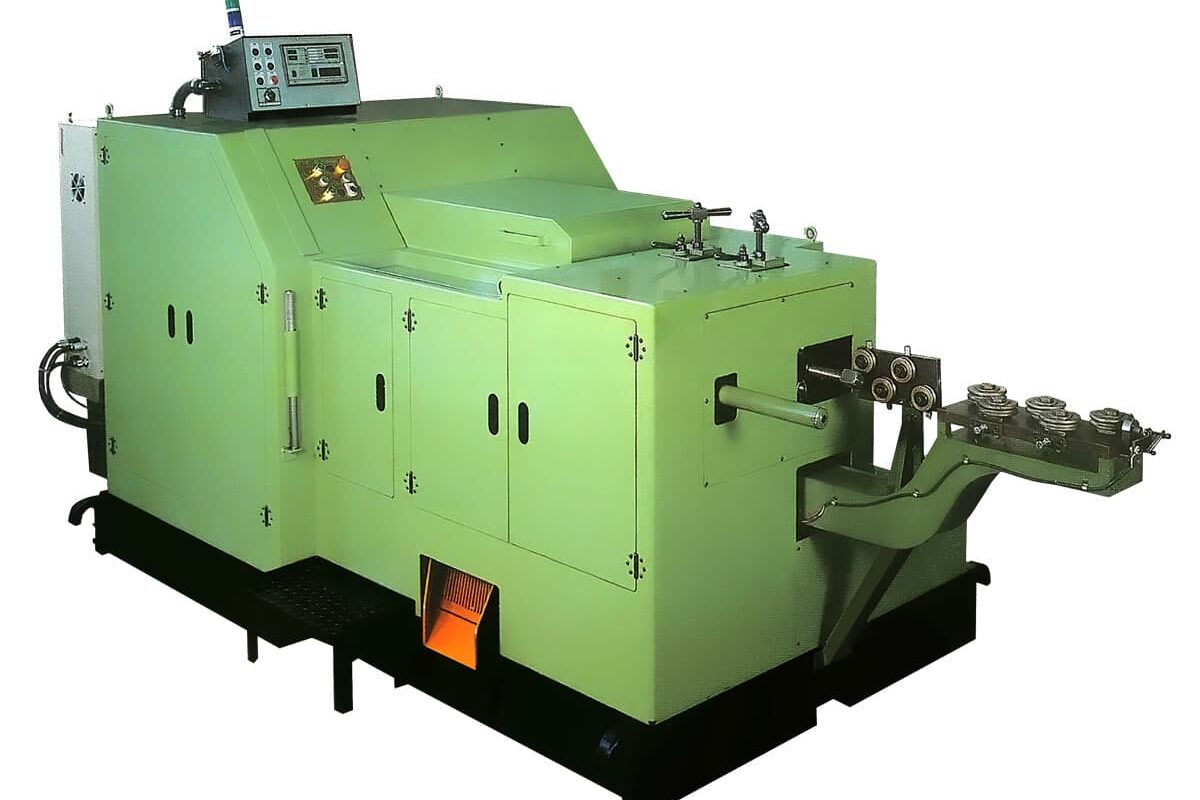
Cold heading machines are one of the most common forming machines used in fastening and industrial applications. These machines utilize the cold heading process to form metal components through the application of compressive force, without involving heat. Cold heading offers various advantages over traditional metal forming techniques and allows for the efficient mass production of high-quality parts.
What is Cold Heading?
Cold heading refers to the metal forming process where sharpened tools are used to push and compress metal stock or wire through a die opening to produce simple parts like bolts, screws, pins, nails, etc. Unlike hot forming processes like forging, cold heading is done at room temperature without applying any heat. The metal stock is placed inside the die and headed by punches that push the metal through the die openings under high compressive forces. This causes the metal to take the shape of the die cavity through plastic deformation without melting or softening the material.
Types of Cold Heading Machines
There are different types of Cold Heading Machine available based on configuration and production requirements:
– Single Stroke Machines: These are basic or entry-level machines suitable for low production volumes. They can produce one part with each stroke of the ram or press.
– Progressive Die Machines: Considered more advanced, they have multiple progressive dies and can produce multiple parts in one stroke through a series of stations. Higher output.
– CNC Controlled Machines: Integrate programmable CNC controls for automation, flexibility and accurate repeatability in part production.
– Full Automatic Machines: Fully automated lines for mass production with automatic feeding, ejection and part handling features.
– Robotic Cold Heading Cells: Combine robotics, automation and CNC controls for lights-out unmanned operation.
Cold Heading Process
The basic cold heading process involves the following steps:
1. Metal Stock Preparation: Raw wire or rods are cut to desired lengths to make blanks for parts.
2. Die Preparation: Dies are precision machined with cavities matching the final part shape and dimensions.
3. Loading the Blanks: Blanks are fed or loaded into the die using an automatic feeding system.
4. Forging Operation: Sharp punches or rams compress the blanks under high pressure through the die cavities.
5. Ejection of Formed Parts: Formed parts are automatically ejected out of the die using ejector pins.
6. Inspection and Finishing: Formed parts undergo quality checks and may require secondary operations.
7. Packaging and Shipping.
Cold heading machines automate this process and enable high-volume production through the synchronized actions of feeding, heading, ejecting, and handling components. The force exerted can be over 200 tons for larger machines. Proper lubrication is also essential for smooth operation and part quality.
Key Advantages of Cold Heading
Compared to traditional metal forming, cold heading offers various production and part quality advantages:
– Does not require pre-heating of metal stock, simplifying the process. Workpieces can be straight from ambient temperature.
– Produces parts with close dimensional tolerances through precise die geometries. Near-net shape components.
– Imparts excellent mechanical properties to the formed part through work hardening and grain refinement.
– Superior surface finish and dimensional consistency in high volumes due to the repeatable process.
– Supports economical mass manufacturing of standardized metal components for various industries.
– Enables forming of harder metals not possible with hot working like hot forging.
– Minimal waste generation as there is no swarf or metal chips from cutting. Negligible heat affected zone.
– Presses and dies can be designed for automatic production with minimum manual intervention.
– Relatively lower initial setup and operating costs versus hot forming techniques.
Cold Heading Applications
Cold heading finds widespread applications across many industries due to the advantages it provides:
– Fasteners: Bolts, screws, nails, rivets used in machinery, construction, automotive etc.
– Automotive: Pins, shafts, gears in transmission, braking and suspension systems.
– Hardware: Staples, hooks, brackets, hinges for furniture, doors and other household goods.
– Electrical: Connector pins, contacts, terminals for switches, relays and other components.
– Tools: Drill bits, seamers, wrenches and various implements.
– Medical: Surgical needles, bone fixation pins and other implants. Also dental tools.
– Agriculture: Nails, spikes used in fencing, woodworking and farming equipment.
– Firearms: Cartridge cases, primers, bullets in ammunition manufacturing.
– Sports Goods: Spikes, pins in shoes, golf clubs, tennis racquets, and other sports accessories.
– Aerospace: Pins, connectors, springs in aircraft cables and instruments.
So in summary, cold heading has emerged as a vital metal forming and net-shape manufacturing process across many critical applications due to its advantages over traditional fabrication methods. Its precision and cost-effectiveness continue to drive further adoption.
Future of Cold Heading Technology
While cold heading has been around for decades fulfilling production needs, the technology will likely see further innovations going forward:
– Advanced die designs using CAE analysis and 3D printing for complex geometries and tighter tolerances.
– Integrated automation with robotic cells, vision systems and adaptive controls for lights-out production.
– CNS/GCC manufacturing capabilities for job shop flexibility and quick changeover/small batches.
– Additive techniques to create composite or near-net shape preforms before heading.
– New forming technologies like flow forming combined with cold heading.
– Cold extrusion development for long/continuous profiles and tubes.
– Biodegradable/sustainable material research for medical and other green applications.
– Condition monitoring, predictive maintenance and data analytics for increased equipment uptime.
– Cold heading simulations using FEM and process optimization techniques.
As demands for quality, efficiency and sustainability increase, cold heading equipment is sure to evolve leveraging the latest manufacturing technologies while keeping its central cost advantages intact. The future remains bright for further innovation and growth in this important industrial segment.
*Note:
1. Source: Coherent Market Insights, Public sources, Desk research
2. We have leveraged AI tools to mine information and compile it