As concerns over air pollution and greenhouse gas emissions continue to rise globally, industries are under increasing pressure to reduce their environmental impact. One technology that has gained prominence in helping heavy industries lower harmful emissions is scrubber systems. In this article, we explore scrubber systems, how they work, their benefits, applications, and the latest developments in this critical emission control technology.
What are Scrubber Systems?
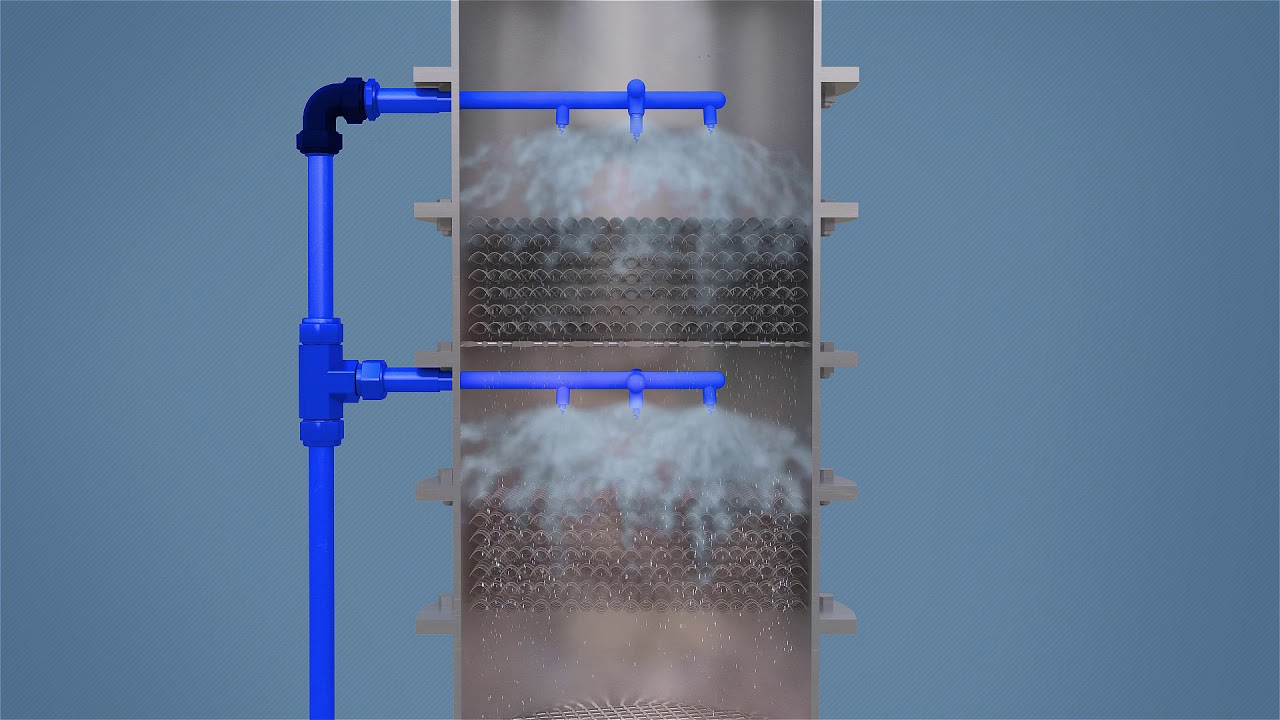
A scrubber system, also known as an air pollution control device, is a device that removes contaminants from industrial exhaust streams using liquid as the scrubbing media. There are various types of scrubbers available depending on the target pollutants and exhaust gas properties. Some common scrubber technologies include wet scrubbers, dry scrubbers, and hybrid scrubbers.
Wet scrubbers use water or alkaline solutions to capture acid gases like sulfur oxides (SOx), hydrogen chloride (HCL), and hydrogen fluoride (HF). The contaminants dissolve or react with the liquid droplets, trapping them before the exhaust is released into the atmosphere. Dry scrubbers use dry reagents like sodium bicarbonate or lime to neutralize and capture acid gases through chemical reactions. Hybrid scrubbers combine aspects of wet and dry technologies.
Benefits of Scrubber System
Scrubber System provide multiple benefits for industries seeking compliance with stringent emission norms. Some key advantages include:
Reduced Emissions: Scrubbers can remove over 90% of SOx, particulate matter (PM), and other target pollutants from flue gases and exhaust streams. This allows industries to meet emission limits and minimize air pollution.
Compliance: Installing scrubbing systems enables compliance with regulations like International Maritime Organization (IMO) rules for sulfur emissions from ships. This ensures legal operations without facing penalties.
Fuel Flexibility: Scrubbers allow industries to continue using high-sulfur fuels that are often cheaper alternatives. Regulations may require switching to low-sulfur fuels otherwise.
Improved Workplace Safety: By reducing airborne contaminants, scrubbers create a healthier work environment with lower occupational hazards for plant staff.
Potential Byproduct Recovery: Some scrubber wastewater can be processed to recover commercially valuable byproducts like gypsum from flue gas desulfurization systems.
Applications of Scrubber Systems
Given their versatility, scrubber systems have widespread industrial applications wherever emissions need control. Some key areas include:
Power Plants: Scrubbers fitted to power plant smokestacks effectively remove SOx, PM and other particulates from coal-fired boiler emissions.
Oil Refineries: Crude processing and catalytic cracking units rely on scrubbers to limit SOx, NOx and other emissions to air.
Cement Manufacturing: Kilns and clinkering operations in cement plants use scrubbers to capture dust and acid gases.
Waste Incineration: Municipal solid waste and medical waste incinerators use scrubbers for flue gas treatment.
Marine Vessels: Marine scrubbers installed on ship exhausts allow continued use of high-sulfur fuel oil within Emission Control Areas.
Latest Developments in Scrubber Technology
With the need for improved emission control growing rapidly, scrubber technology continues advancing towards higher efficiency, smaller footprints, and new applications. Here are some key ongoing developments:
Hybrid/Multi-Pollutant Scrubbers: Combination wet/dry systems that can remove multiple pollutants simultaneously with one unit, including SOx, NOx, PM and mercury.
Seawater Scrubbing: Marine scrubbers using seawater as solvent eliminates discharge of contaminated washwater. Adaptable for various vessel types and fuels.
Modular/Skid-Mounted Systems: Smaller, modular scrubber designs make installation simpler for retrofitting and modular plants. Easier logistics and maintenance.
Non-Thermal Plasma Scrubbers: Advanced plasma-based systems show potential for higher pollutant removal rates, especially for reactive gases like NOx and dioxins.
Bio Scrubbers: Under research, biomass-fueled scrubbers may offer new opportunities for emission control in future with lower operating costs.
New Applications: R&D focuses on adapting scrubbers for novel uses like VOC control from coating/painting lines, 3D printing fume treatment and agricultural applications.
As emission norms get stricter globally, scrubber systems will remain a vital technology helping heavy industries curb air pollution at source. Ongoing advances are making scrubbers more effective, flexible and practical to deploy across a wider range of industrial processes. With the technology now proven at commercial scale worldwide, scrubbers can be expected to play an expanding role in environmental protection and regulatory compliance in the decades ahead.
*Note:
1. Source: Coherent Market Insights, Public sources, Desk research
2. We have leveraged AI tools to mine information and compile it