The Rise of Robotic Assistants in Stores
In recent years, robotic assistants have started to make their way into retail stores to provide customer service and support various tasks. One of the earliest examples was Lowe’s deployment of robotic floor cleaners called Tillie in 2017. These robots could vacuum, mop, and scrub store floors automatically around the clock. They helped reduce the time spent on manual cleaning and allowed staff to focus on assisting customers. Other major retailers like Walmart, Kroger, and Target have also experimented with robots for tasks like shelf scanning, product sorting, and inventory monitoring.
Robots Providing Customer Service and Guidance
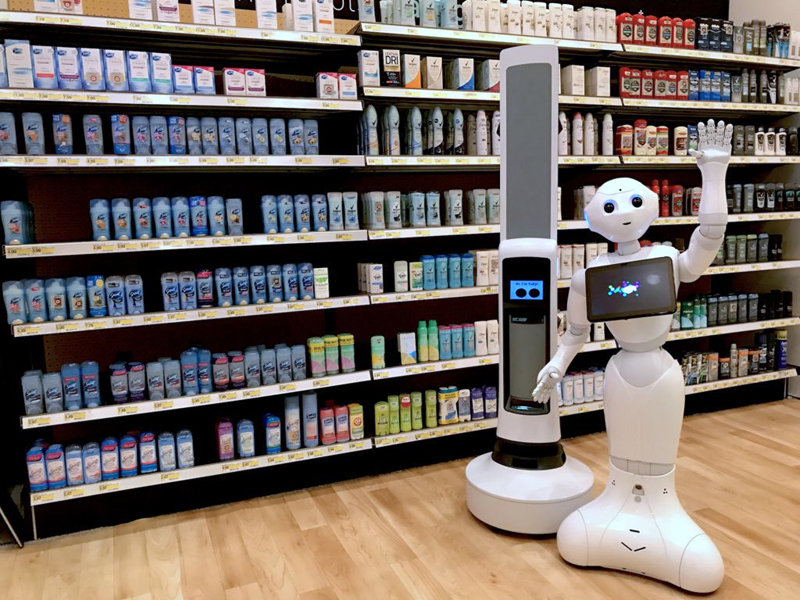
Some stores have introduced Retail Robots that can directly interact with and assist customers. One popular model is the guided shopping robot GuidiGo, which has been deployed by Panasonic in several of its stores in Japan. The robot acts as a roaming assistant that can answer basic product questions and direct customers to specific aisles or sections. It is equipped with cameras, microphones, and a touchscreen to facilitate interactions. International retailers are also experimenting with robotic advisors. For example, Soft Bank launched the robot Pepper to greet customers and provide information about available products and services at its brand stores across Asia.
Automated Delivery Robots in Stores
Another emerging application of robots is for internal product deliveries within large retail stores. For example, robots created by Russian company Cyberunit can deliver products between stockrooms and checkout areas to speed up order fulfilment. Major online retailers like Amazon are also testing delivery robots. The Amazon Scout robot is a small, quiet, and electricity-powered device that can navigate sidewalks and deliver packages within a neighborhood. This allows for contactless delivery, which is helpful during situations like the ongoing pandemic. Several grocery stores are piloting delivery robots to drop off orders in customer vehicle trunks or at their doorsteps.
Machines Taking Over Backroom Tasks
While customer-facing robots are the most visible examples, the bulk of robotic automation in retail is actually happening behind the scenes. Many routine backroom jobs like unpacking delivery boxes, sorting items, and fulfilling online orders are now handled by robots. For instance, Amazon uses hundreds of thousands of robots called drive units in its fulfilment centers. Mounted with totes and bins, these automated machines ferry products between stations and assist workers in picking, packing and shipping orders efficiently. Robotics companies like Clearpath have developed sorting systems that can identify incoming products and route them for breakdown and restocking in warehouses. This automation improves productivity, reduces error rates, and helps cope with demand spikes.
Job Impacts of Retail Robotics
Naturally, increased robotic automation has implications for retail jobs. While some roles become redundant, new types of jobs are also being created to manage and maintain these automated systems. Skill requirements are evolving as well, with a greater emphasis on technical competencies. Cashier roles especially have significantly declined due to self-checkout kiosks and apps. However, growing demand for technical support staff, robot programmers and data analysts means that the number of overall jobs is not decreasing drastically in most cases. Some experts predict that automation may eliminate up to 30% of existing retail roles in the long run but also enable the creation of new rewarding career opportunities.
Customer Responses to Shopping with Robots
Surveys suggest that customers have generally positive impressions of robots fulfilling utilitarian jobs like product locating, inventory checks or deliveries that save time. However, they still prefer personal guidance for complex tasks like payments or recommendations from human associates they can interact with. Retailers need to carefully consider what applications are suitable for robotic assistance versus direct human engagement. Cultural differences also factor in – while Japanese consumers seem very open to shopping companion robots, some Western customers still find the idea intrusive or impersonal. Overall familiarity and education can alleviate privacy or job replacement concerns regarding retail robotics over time.
The Future of Retail Automation
Looking ahead, robotics technologies will further penetrate retail environments. Advancements in areas like computer vision, AI, and mobility will enable robots to take on more complex jobs involving decision making, logistics coordination and personal interactions. Experts anticipate a growing for collaborative robots that can work alongside human employees safely. Self-driving vehicles may deliver shipments between warehouses, while delivery drones speed up last-mile transportation of purchases. Miniature drones and bots may one day roam store aisles to answer questions or fetch out-of-stock items on demand. Increased automation could help retail adapt to trends like rising wages, labor shortages and growing fulfillment complexities in the online channel. While it may disrupt some traditional jobs, it also brings new opportunities for the industry and its workforce to evolve in this digital era.
Robotic systems have started augmenting various tasks across the retail value chain from warehouses to sales floors. While still limited to structured environments, they are gradually handling more complex jobs with advancements in enabling technologies. Public perceptions are also shifting as robots become a familiar part of the shopping experience. Both retailers and customers stand to gain many benefits from judicious application of automation in terms of efficiency, cost savings as well as convenience. It will be interesting to see how this transformation evolves in diverse global markets and store formats in the coming years.
*Note:
1. Source: Coherent Market Insights, Public sources, Desk research
2. We have leveraged AI tools to mine information and compile it