The healthcare industry is constantly evolving with new technologies that make diagnosis and treatment more accessible and convenient for patients. Portable medical devices are revolutionizing how healthcare is delivered by allowing tests and monitoring to be done outside of clinical settings. These innovative devices are poised to transform the healthcare experience for both providers and patients in the years to come.
History of Portable Devices
Portable medical devices were initially developed to address specific acute care needs that required monitoring outside of hospitals. Some of the earliest portable devices included electrocardiogram (ECG) machines in the 1960s, which allowed cardiologists to monitor heart activity outside of medical facilities. Through advances in miniaturization of electronics and new power sources like batteries, additional portable devices were created over the following decades. Developments in wireless transmission of medical data also boosted the capabilities of portable devices. Today, there are portable options available for various diagnostic tests, patient monitoring, emergency response, and more.
Key Types of Portable Devices
Emergency Response Devices
Portable defibrillators were among the first emergency response devices developed to treat cardiac arrest outside of hospitals. Modern automatic external defibrillators (AEDs) can now be found in many public places like airports due to their ease of use. Other emergency response devices include portable ultrasound machines, which can assist first responders and military medics in diagnosing injuries in the field.
Patient Monitoring Equipment
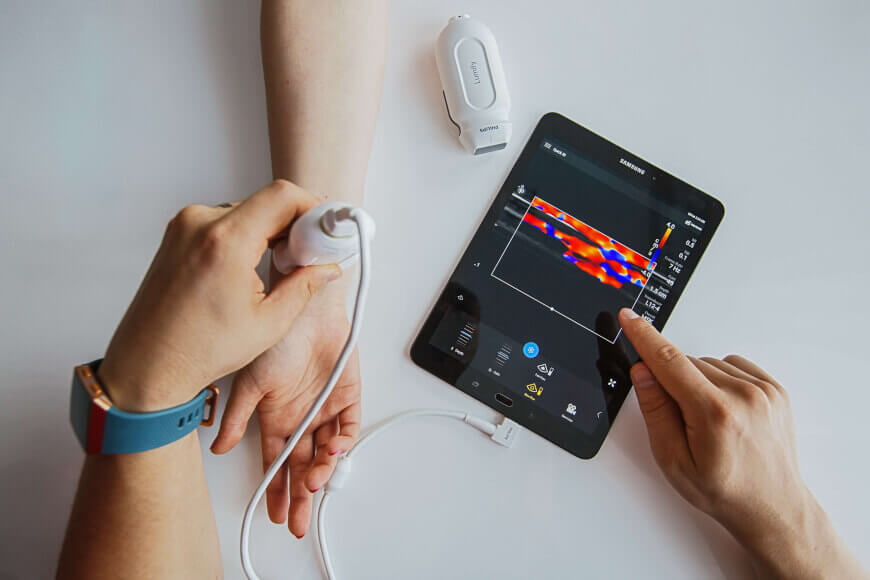
Wearable devices and patches have revolutionized remote Portable Medical Devices. Continuous glucose monitors allow diabetics to wirelessly track blood sugar levels anywhere. Portable ECG and heart rate monitors make it simple for patients to self-monitor cardiac activity and share readings with doctors. Miniaturized pulse oximeters can measure blood oxygen levels on the go. With cellular and Bluetooth connectivity, these devices transmit health stats to clinicians in real-time.
Diagnostic Testing Devices
Now portability has expanded diagnostic testing beyond doctors’ offices as well. Handheld ultrasound scanners, endoscopes, otoscopes and other examination tools enable primary evaluations to occur in alternative settings. Miniaturized cancer screening machines can detect tumors in places where full-size equipment can’t reach. Portable X-ray and CT machines even perform imaging in the field or for populations lacking access to hospitals.
Therapeutic and Rehabilitation Devices
Portable nebulizers, infusion pumps and other therapeutic devices allow treatment regimens to continue outside clinical supervision. Some patients can now manage complex conditions like diabetes independently thanks to wearable artificial pancreases. Rehabilitation tools like portable motion sensors and virtual reality headsets also help move therapy beyond therapy rooms.
Benefits of Portable Medical Technology
Increased Patient Access and Convenience
With the ability to conduct tests, screenings and monitoring at home or on the go, portable devices eliminate transportation barriers that previously limited access to healthcare services. This empowers patients to proactively manage their health in everyday life versus office visits alone. It also relieves overburdened health systems.
Accelerated Triage and Diagnosis
Emergency use of portable ultrasounds, artificial intelligence-based imaging devices, and other diagnostic tools enables paramedics and first responders to rapidly assess patients on scene and relay critical details to awaiting hospital teams. This facilitates timelier treatment decisions that can make the difference between life and death.
Advanced Remote Monitoring and Care
Continuous data streaming from wearable monitoring devices allows clinical evaluation to virtually extend beyond physical exam rooms. Physicians gain deeper insights into patients’ real-world health trends over time versus isolated office visits. telehealth also empowers management of chronic conditions in remote or rural areas facing provider shortages.
Support for Independent Living and Aging in Place
As people seek to age with dignity in their own homes, portable medical tech is easing the transition by bringing advanced diagnostics and therapeutic capabilities into living spaces. Features like fall detectors and remote patient monitoring give seniors and their families peace of mind while maintaining independence.
Barriers to Broader Adoption of Portable Devices
While portable medical devices offer clear advantages, several challenges still hinder their optimal integration into mainstream healthcare delivery:
Interoperability Issues
Many existing portable devices cannot seamlessly interface with electronic health records or share data between different manufacturers’ products due to incompatible systems. This limits the utility of collected health data.
Reimbursement Realities
Insurance rarely covers the costs of consumer-oriented portable medical devices, restricting adoption rates. Policies also often lag behind rapid product innovations, leaving clinicians uncertain if testing outside traditional settings will be compensated.
Device Validation
Rigorous validation of portable devices’ accuracy, precision, reliability, and clinical usefulness compared to larger stationary equipment is still ongoing for many novel models. Physicians remain cautious about dependence on unproven technologies.
Connectivity Constraints
Reliable data transmission depends on consistent wireless connectivity that may be sparse in remote regions where portability is most impactful. Glitches disrupt real-time monitoring and transmission of test results.
User Experience Hurdles
Clear guidelines and educational tools are still needed to guarantee patients understand how to properly self-administer tests or use complex portable machines optimally independent of medical supervision. Device designs must accommodate varying technical skill levels and disabilities.
Overcoming these challenges will require coordinated efforts between innovators, regulatory agencies, healthcare payers and providers. Standards like integrated digital interfaces, certifications of portable device performance, provider education, and guaranteed payment models can pave the way for mainstream assimilation.
Future of Portable Medical Innovation
As 5G networks and edge computing progress, patient monitoring and diagnostic devices are poised to become even more precisely miniaturized yet powerful. Virtual and augmented reality capabilities may transform rehabilitation, medical training and telesurgery. Biosensors embedded directly under the skin promise to seamlessly and continuously track biometrics without discomfort. Artificial intelligence will help clinicians efficiently extract actionable insights from floods of patient-generated health data. Drones, robots and other automated technologies may extend the reach of medical care into most remote areas worldwide. Portable medical technologies are undoubtedly breaking down boundaries to reshape healthcare delivery according to individual needs rather than limitations of institutional settings alone. The changes ahead will elevate standards of care accessibility and quality worldwide.
Portable medical devices have made tremendous progress expanding opportunities for testing, monitoring and treatment outside traditional clinical facilities. While challenges still constrain their full realization, concerted efforts to optimize standards, validation, education, coverage and connectivity should further mainstream these technologies’ adoption. Ultimately, portable innovations will equip people with unprecedented independence and empowerment in managing health throughout daily living wherever circumstances take them.
*Note:
1. Source: Coherent Market Insights, Public sources, Desk research
2. We have leveraged AI tools to mine information and compile it