Hyperthermia, Which Literally Means ‘High Temperature’, Is An Emerging Cancer Treatment That Uses Heat To Damage And Kill Cancer Cells Or Sensitize Them To Other Treatments Like Chemotherapy, Radiation Therapy, Immunotherapy And More. In This Article, We Will Explore In Detail About Hyperthermia Cancer Treatment Including How It Works, Its Benefits, Types And More.
What Is Hyperthermia Cancer Treatment?
Hyperthermia Is A Type Of Cancer Treatment That Exposes The Body Or A Specific Tumor Area To High Temperatures Slightly Higher Than Normal Body Temperature. Normal Body Temperature Is Around 98.6°F (37°C) While Hyperthermia Treatment Heats The Body Or Tumor Area Up To Around 106°F (41°C). This Mild Increase In Temperature Is Enough To Damage And Kill Cancer Cells Or Make Them More Vulnerable To Other Treatments Without Affecting Normal Cells.
Hyperthermia Cancer Treatment Works Based On The Fact That Cancer Cells Are Generally More Vulnerable To Heat Than Normal Cells. When The Body Is Heated To 106°F, It Can Interfere With Cancer Cell’s Protein Structure And Damage Their Cellular Machinery Making It Difficult For Them To Continue Growing And Spreading. This Mild Fever Range Heat Is Usually Well Tolerated By Normal Tissues.
Hyperthermia Cancer Treatment
There Are Three Main Types Of Hyperthermia Treatments Based On How It Is Localized And Administered:
Local Hyperthermia: In This Type, Heat Is Applied Only To The Tumor Site Using Interstitial Probes, Microwave Antennas Or Electromagnetic Induction Devices. This Accurately Treats The Tumor Without Increasing Body Core Temperature.
Regional Hyperthermia: Here, Heat Is Applied To An Entire Body Area Or Limb Containing A Tumor. It Uses Techniques Like Electromagnetic Or Capacitor Heating To Raise The Temperature Of A Body Region Without Significantly Impacting Other Areas.
Whole Body Hyperthermia: This Involves Heating The Entire Body To Slightly Elevated Temperatures Using Methods Like Hot Water Blankets, Heating Pads Or Radiant Heat Lamps Placed Around The Body. Core Body Temperature Is Increased By 1-2°C (1.8-3.6°F).
Benefits And Effectiveness Of Hyperthermia Cancer Treatment
Hyperthermia Has Several Benefits As A Cancer Treatment. Some Of The Major Benefits Are:
– Sensitizes Cancer Cells To Chemotherapy And Radiation: Heating Tumors Enhances The Effects Of Chemotherapy Drugs And Radiation Therapy By Making Cancer Cells More Vulnerable To Their Effects. This Allows Lower Doses Of Chemo/Radiation To Be Used.
– Direct Cancer Cell Killing: Mild Heating To 41-45°C Causes Protein And Structural Damage Within Cancer Cells Leading To Cell Death. Tumor Cells Are Generally More Heat-Sensitive Than Normal Cells.
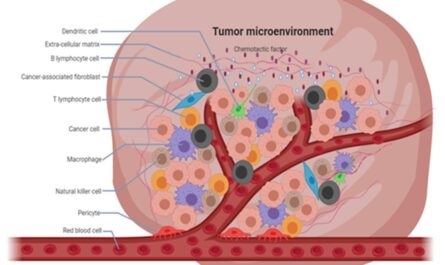
– Improves Immune Response: Hyperthermia Boosts The Body’s Immune Response Against Cancer Cells By Making Heat Shock Proteins On Cancer Cells More Visible To Immune Cells. This Helps Immune Cells Better Target Tumors.
– Non-Invasive: Hyperthermia Treatment Does Not Require Surgery Or Cutting Into The Body. Various External Devices Are Used To Heat Tumor Areas/Body In A Non-Invasive Manner.
– Effective Against Various Cancers: Hyperthermia Has Shown Promise In Treating Cancers Like Breast Cancer, Melanoma, Head & Neck Cancers, Cervical Cancers Etc. Especially When Combined With Chemotherapy/Radiation.
– Potentially Curative: When Administered Along With Radiation Therapy Or Chemotherapy, Hyperthermia Has The Potential To Cure Some Localized Solid Tumors Entirely In Certain Cases.
Potential Side Effects And Limitations
While Hyperthermia Is Generally Well Tolerated, Some Potential Side Effects May Include:
– Discomfort, Pain Or Burning Sensation At The Heated Area During Treatment.
– Fatigue, Weakness, Nausea Or Vomiting In Some Patients Undergoing Whole Body Hyperthermia.
– Rarely, Superficial Skin Burns May Occur At The Heated Tumor Site In Case Of Local Hyperthermia.
– Organ Damage Is A Very Small Risk If Body Temperature Rises Above 107°F During Whole Body Hyperthermia. Strict Safety Protocols Are Followed.
Currently, Limitations Include Inability To Heat Deep-Seated Tumors Effectively And Difficulty Cooling Organs Closer To Heated Tumor Areas Which Can Potentially Impact Their Functions. Ongoing Research Aims To Overcome These Limitations Through Novel Techniques And Devices.
The Future Of Hyperthermia Cancer Treatment
With Ongoing Research, Hyperthermia Is Emerging As An Important Complementary Or Adjuvant Treatment To Mainstream Options Like Chemotherapy, Radiation Therapy Or Immunotherapy. Some Key Developments And Future Directions Include:
– New Localized Heating Methods Like Magnetic Or High Intensity Focused Ultrasound Hyperthermia For Better Targeting Of Deep Tumors.
– Integration Of Real-Time Imaging And Temperature Monitoring For Precise Control And Safety.
– Combined Therapies With Immunotherapy To Boost Anti-Cancer Immune Response.
– Multi-Institutional Clinical Trials To Better Establish Safety And Effectiveness.
– Adaptive Hyperthermia Using Automated Tumor Feedback To Control Heating Parameters For Individual Patients.
– Development Of Nano-Platforms For Targeted Drug Delivery Activated By Localized Hyperthermia.
– Integration Of Hyperthermia Into Cancer Treatment Algorithms As A Standard Adjuvant Therapy Based On Clinical Outcomes.
Hyperthermia Shows Great Potential Against Various Cancers And Represents An Innovative Non-Invasive Means To Kill Cancer And Boost Other Treatments. With Ongoing Research And Clinical Adoption, Hyperthermia Could Become Part Of Mainstream Cancer Care Algorithms In The Future.
1. Source: Coherent Market Insights, Public sources, Desk research
2. We have leveraged AI tools to mine information and compile it.