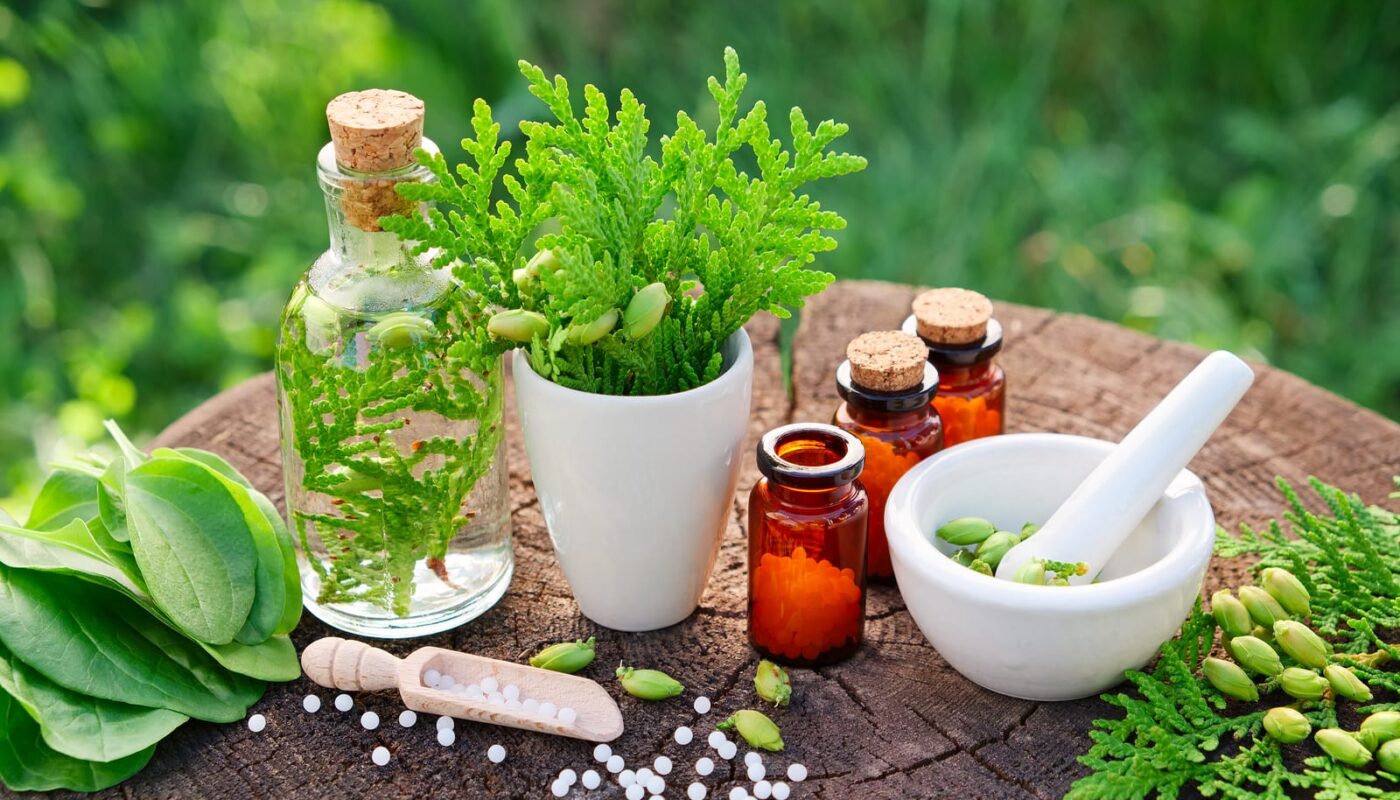
Traditional medicine refers to health practices, approaches, knowledge and beliefs incorporating plant, animal and mineral based medicines, spiritual therapies, manual techniques and exercises, applied singularly or in combination to treat, diagnose and prevent illnesses or maintain well-being. While modern medicines have made considerable progress, a large section of global population still relies on traditional medicine for their primary healthcare. Let us look at some key aspects of global traditional medicine and its contributions.
Diverse Systems of Traditional Medicine
Around the world, many indigenous cultures have developed their own traditional medical practices built upon centuries of knowledge and experience. Some major global systems of traditional medicine include:
– Chinese Traditional Medicine (TCM): Originating in China, it is one of the oldest medical systems in the world relying on acupuncture, herbal remedies, tai chi and qi gong. TCM views illness as imbalance in energy flow.
– Ayurveda: Evolved in the Indian subcontinent over 5,000 years, it emphasizes preventive healthcare through diet, lifestyle, yoga and herbs. Ayurveda treats each person uniquely based on their constitution or prakriti.
– Traditional African Medicine: Global Traditional Medicine Encompasses diverse ethnic based practices across Africa using botanical preparations, spiritual cleansing and community healing approaches.
– Native American Medicine: Incorporates plant-based remedies, rituals and energy healing practices of North and South American indigenous populations. Sweat lodges and herbal treatments feature prominently.
– Arabic Unani Medicine: Derived from Greco-Arabic traditions practiced since medieval times in West and South Asia and parts of Africa. It relies on herbs, diet and lifestyle therapies.
Global Reach and Acceptance
Despite advances in modern scientific medicine, traditional systems continue to be the most accessible and affordable form of healthcare for nearly 80% people worldwide, especially in developing and underdeveloped regions according to the WHO.
– In China, over 200 million people use TCM annually with its hospitals and clinics widespread. Acupuncture is also popular in the West.
– Ayurveda maintains popularity in India and among yoga communities globally. Its products constitute a $10 billion+ industry in India alone.
– African traditional medicine supports over 80% primary healthcare on the continent given its economic viability in rural areas.
– Native American healing practices see a revival among local communities and certain lifestyle therapies gain global acceptance.
– Unani medicine remains an integral part of medical pluralism in many Asian and African countries.
Contributions to Modern Therapeutics
While evidence basis of some traditional practices is still being investigated, significant contributions to modern therapies have already emerged from traditional knowledge:
Natural Products Development
– Over 80% of world’s population depends on herbal medicine. Global herbal medicine market was estimated at $83 billion in 2018.
– Drugs derived from traditional therapies include artemisinin (malaria), taxol (cancer), codeine, quinine, aspirin, morphine and many more.
– Natural compounds in turmeric, garlic, citrus, ginger, neem, holy basil etc. show promise against various ailments.
Disease Management Techniques
– Acupuncture/acupressure established for pain, nausea and rehabilitation. Several yoga postures aid musculoskeletal issues.
– Meditation, tai chi, massage therapies adopted to reduce stress, anxiety, depression and enhance well-being.
Preventive Healthcare Model
– Traditional diets, routines promote overall health as per balance of energies/doshas rather than focusing on disease alone.
– Lifestyle changes recommended to strengthen immunity and resistance to infections rather than just curing.
Integration with Mainstream Medicine
With further validation of traditional techniques and compounds through research, their safe integration with allopathy can expand medical pluralism and patient access to affordable healthcare worldwide. Many nations already promote such combinatorial models.
*Note:
1. Source: Coherent Market Insights, Public sources, Desk research
2. We have leveraged AI tools to mine information and compile it