The global emissions trading market is estimated to be valued at US$334.80 billion in 2023 and is expected to exhibit a CAGR of 24% over the forecast period 2023-2030, according to a new report published by Coherent Market Insights.
Market Overview:
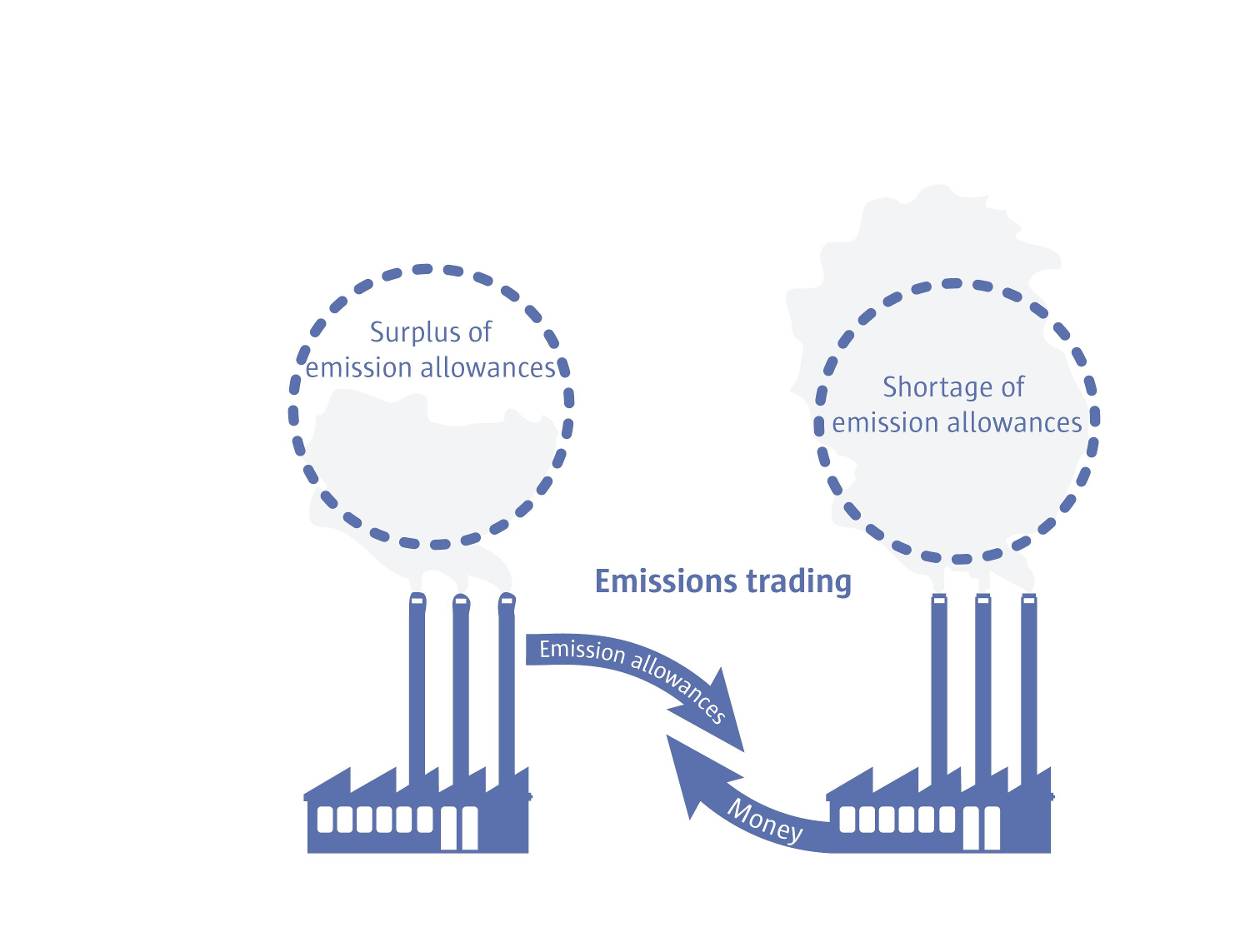
The emissions trading market involves the buying and selling of emission permits, allowing organizations to reduce their greenhouse gas emissions. This market offers an effective mechanism for governments to tackle climate change and achieve sustainable development goals. The need for products and solutions associated with emissions trading is increasing as organizations worldwide are striving to reduce their carbon footprint and comply with emission reduction regulations. Emissions trading offers advantages such as flexibility, cost-effectiveness, and environmental sustainability.
Market Key Trends:
One key trend in the emissions trading market is the growing adoption of carbon pricing initiatives by governments across the globe. Carbon pricing aims to internalize the environmental cost of greenhouse gas emissions by imposing a financial penalty on polluters. This trend is driven by the increasing awareness of climate change and the need for sustainable practices. Carbon pricing initiatives, such as carbon taxes and cap-and-trade systems, encourage organizations to reduce their emissions and invest in green technologies. This trend is expected to drive the demand for emissions trading in the coming years.
Porter’s Analysis
Threat of New Entrants:
The emissions trading market presents a moderate threat of new entrants due to high capital requirements and government regulations. The complexity and scale of establishing emissions trading platforms act as barriers to entry, limiting the influx of new players.
Bargaining Power of Buyers:
Buyers in the emissions trading market hold limited bargaining power due to the crucial role compliance plays in meeting emission reduction targets. As a result, buyers have little room for negotiation and are inclined to accept prevailing prices set by the market.
Bargaining Power of Suppliers:
Suppliers, primarily carbon credit generators and brokers, possess significant bargaining power. The limited availability of verified emission reduction units and the demand-supply gap amplify their ability to influence prices and terms of trade. However, the emergence of new technologies and sustainable practices can potentially lower their power.
Threat of New Substitutes:
The threat of substitutes in the emissions trading market is moderate. The growing focus on renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind, may encourage businesses to invest heavily in clean technologies and reduce their reliance on emissions trading for compliance. However, the established infrastructure and established market mechanisms of emissions trading serve as strong barriers to substitute industries.
Competitive Rivalry:
Competitive rivalry is intense within the emissions trading market. Key players compete for market share, trading volumes, and access to carbon credits. The presence of large multinational corporations, financial institutions, and specialized firms contributes to the competitive landscape with strategies like mergers, acquisitions, and collaborations.
Key Takeaways
The global emissions trading market is expected to witness high growth, exhibiting a CAGR of 24% over the forecast period (2023-2030). This growth is primarily driven by increasing environmental concerns, evolving regulatory frameworks, and the transition towards a low-carbon economy. Emissions trading provides an effective mechanism to achieve emission reduction targets and incentivize sustainable practices among businesses.
In terms of regional analysis, Asia Pacific is expected to be the fastest-growing and dominating region in the emissions trading market. The rising industrial activities, rapid urbanization, and stricter emission regulations in countries like China, India, Japan, and South Korea drive the demand for emission trading instruments.
Key players operating in the emissions trading market include BP Plc, Royal Dutch Shell Plc, Total SE, Chevron Corporation, ExxonMobil Corporation, Engie SA, RWE AG, ON SE, Vattenfall AB, Gazprom, Mitsubishi UFJ Financial Group (MUFG), JPMorgan Chase & Co., Goldman Sachs Group, Inc., Citigroup Inc., and Barclays PLC. These players possess extensive experience, global reach, and financial capabilities, allowing them to navigate complex market dynamics and offer integrated solutions to clients.
In conclusion, the emissions trading market presents a promising landscape for investors, governments, and businesses aiming to mitigate climate change and achieve sustainability goals. The market’s steady growth, coupled with the dominance of key players and regions, provides ample opportunities for stakeholders to explore and capitalize on the potential of emissions trading.
*Note:
1. Source: Coherent Market Insights, Public sources, Desk research
2. We have leveraged AI tools to mine information and compile it