The Advent of Battery-Powered Transport
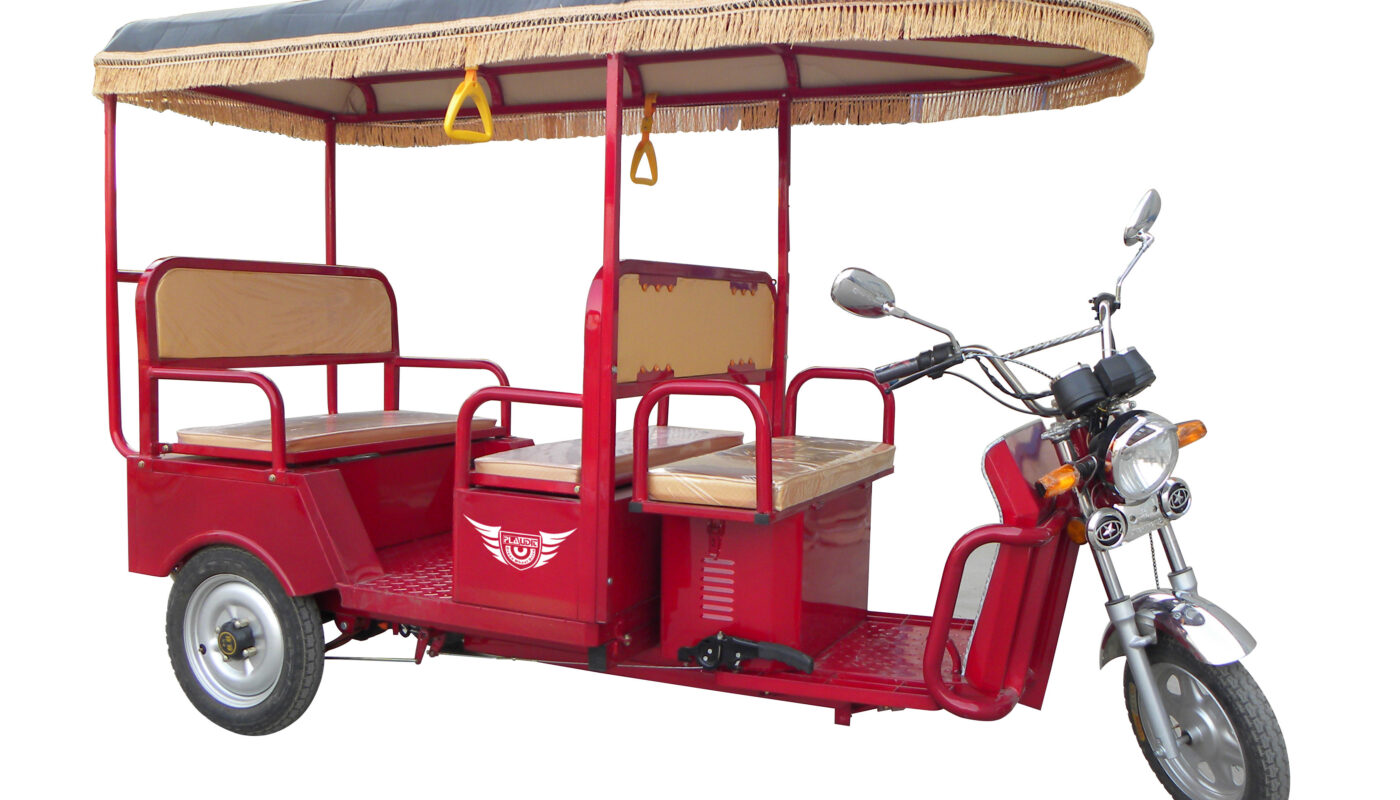
E-rickshaws are one of the newest forms of public and commercial transport to emerge across Indian cities in recent years. An e-rickshaw, or battery-powered rickshaw, runs entirely on a lithium-ion battery that is charged overnight. This allows e-rickshaws to travel distances of up to 50-60 km on a single charge depending on factors like load, terrain and driving habits. Compared to traditional auto-rickshaws that run on petrol or CNG, e-rickshaws have significantly lower operational costs since electricity is cheaper than fossil fuels in the long run. They are also more environmentally sustainable as they do not emit harmful gases. This has made e-rickshaws an attractive alternative for both passengers and drivers.
Rising Popularity Among Commuters
E-Rickshaw have gained widespread popularity among city commuters for short-distance trips within 5-7 km. They are convenient, affordable and cause less traffic congestion compared to other modes of transport. The comfortable seating and slow pace of travel also make e-rickshaws preferable for the elderly, women and children. As a result, they have become the preferred last-mile connectivity solution in big cities and towns across India. In Delhi alone, over 100,000 e-rickshaws are plying on the streets according to recent estimates. Other metropolitan regions like Bengaluru, Mumbai, Kolkata and Chennai have also seen a surge in e-rickshaw numbers to meet growing intra-city transportation needs.
Benefits for Drivers and Owners
Another key reason for the rise of e-rickshaws is that they provide a viable source of livelihood for many. With only a modest initial investment of around Rs. 1-1.5 lakhs needed to purchase an e-rickshaw, individuals from low-income households can easily take up driving as an occupation. On average, e-rickshaw drivers earn anywhere between Rs. 300-500 per day by working 8-10 hours, which is higher than most informal jobs. Importantly, there are low running costs since electricity is cheaper than petrol by more than half. Routine maintenance expenses are also minimal compared to fuel-run vehicles. Over time, e-rickshaw owners recover the initial investment and are left with a valuable asset. This has spurred many entrepreneurs to set up e-rickshaw fleets for commercial operations across major cities.
Government Support and Regulatory Changes
Given the environmental and socio-economic benefits of e-rickshaws, the central and state governments have extended policy support to promote their adoption. In 2015, the Delhi government legalized the plying of e-rickshaws and issued permits to over 27,000 drivers. This boosted their numbers multifold within a few years. Other states like Maharashtra, West Bengal, Uttar Pradesh and Bihar have followed suit with similar recognition. Financing schemes offered by NABARD and other banks have made purchase of an e-rickshaw easier on credit. Further, the Faster Adoption and Manufacturing of Electric Vehicles (FAME) initiative by the Department of Heavy Industries provides purchase incentives of up to Rs. 30,000 per e-rickshaw. This has encouraged local production and significant price reductions over time.
Addressing Challenges
While e-rickshaws have taken Indian cities by storm, there are still infrastructural and regulatory challenges that need addressing. Chief among these are issues around separate lanes, parking spaces and safety standards. With unregulated growth, e-rickshaws often end up obstructing traffic or operating in an unsafe manner without basic safety features like seat belts, brakes and speed governors. Concerns have also been raised about the use of lead-acid batteries and improper disposal. To fully realize their potential, city administrations will need to put in place dedicated lanes, designated parking zones and enforce compliance with safety norms uniformly. Battery manufacturers are working on developing affordable lithium-ion alternatives. If these issues are appropriately tackled, e-rickshaws could evolve into a mainstay for urban transportation over the next decade.
The Way Forward
Overall, e-rickshaws represent an important milestone in India’s shift towards more sustainable solutions for mobility. By addressing first and last-mile connectivity needs of communities effectively, they have proven far more accessible than conventional metro and bus services. Going forward, with continued governmental support and policy refinement, the volume of e-rickshaw sales as well as ridership is expected to rise manifold. As costs fall with increased local production, wider diffusion into smaller cities and towns can be achieved. As technologies advance, battery life will increase while prices reduce further. This will cement the position of e-rickshaws as the preferred public transport mode, helping realize India’s vision of electric mobility at grassroots levels. Barring unforeseen disruptions, e-rickshaws are poised to transform public transportation across India in the decades to come.
*Note:
1. Source: Coherent Market Insights, Public sources, Desk research
2. We have leveraged AI tools to mine information and compile it.