Dentistry has come a long way from the days of hand tools and basic mirrors. Today’s dental practices rely heavily on advanced technology to provide high-quality care. One crucial piece of modern dental equipment is the dental camera. These specialized cameras allow dentists to thoroughly examine patients’ teeth and oral health in new ways that weren’t previously possible.
Intraoral Cameras
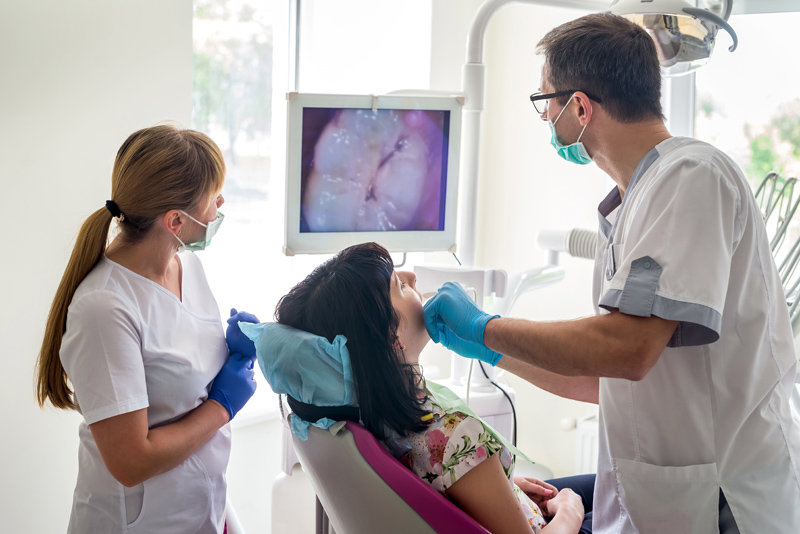
Perhaps the most common type of dental camera is the intraoral camera. As the name suggests, these cameras are designed to be inserted directly into a patient’s mouth during an exam. Typical intraoral cameras are small, lightweight devices mounted on the end of a pen-like handle. The camera sensor is located at the tip, allowing dentists to maneuver it between teeth and gums to capture digital images.
Magnification is a key advantage of intraoral cameras. While traditional mirrors only provide about 2x magnification, these cameras can magnify images up to 20x or more. This level of magnification enables dentists to spot even the smallest cavities, cracks, plaque deposits, and abnormalities that might otherwise be missed. The cameras also feature built-in LED lighting to illuminate dark areas of the mouth for clearer images.
Beyond improved visibility, intraoral cameras deliver another benefit – they eliminate the mirrored view dentists see in traditional mirrors. The cameras’ displays show dentists an anatomical view of the teeth and mouth from the patient’s perspective. This correlates better with what the patient sees, improving communication during exams and treatment planning discussions. Many practices now incorporate camera monitors into their operatories so patients can also view examination findings with the dentist.
Digital Radiography
Dental x-rays, also called dental radiographs, provide important diagnostic information about the internal structures of teeth and surrounding bone. While film-based x-rays were the norm for decades, modern practices are transitioning to digital radiography systems featuring specialized x-ray sensors and dental cameras.
These digital sensors snap radiographic images in seconds, without the need for developing chemicals. The captured x-ray data is immediately visible on connected computer monitors without delay. Digital sensors are smaller than film, enabling dentists to obtain more precise images of individual teeth or limited areas of the mouth. Digital x-rays expose patients to up to 90% less radiation than conventional films, offering a safer alternative.
An integral component of digital radiography setups is the dental camera. Most systems house a small radiation sensor that functions similarly to a camera’s image sensor. When x-rays pass through the mouth, the camera records the data and transmits the digital radiograph file to a computer. Dentists can then examine, save, and even electronically share the images instantaneously using camera software – a major upgrade over waiting to develop films. Digital cameras allow practices to transition to a paperless record-keeping system with all patient x-raysarchived digitally.
Intraoral Cameras Improving Communication
While diagnostic capabilities are a huge benefit, dental cameras also enhance communication between dentists and their patients. Large displays connected to intraoral cameras let dentists clearly show patients abnormalities, problem areas, plaque and calculus deposits highlighted during exams.
Patients who may feel apprehension about procedures can better understand what is truly involved when they can view proposed treatments, decay locations, planned restorations and more on camera monitors. Before-and-after images provide powerful proof of a treatment’s effectiveness. With cameras, dentists can take patients on a “visual journey” through their oral health concerns and solutions.
Modern Dental Cameras patients especially value the interactive, clearer communication style facilitated by cameras. Instead of relying solely on clinical descriptions, practices can engage visual learners by pulling up magnified views during discussions. Patients leave visits better informed about their oral health status and next steps when cameras objectively demonstrate examination findings. The result is improved understanding, reduced anxiety and increased likelihood of caring for problems early before they escalate.
Teeth Whitening and Aesthetic Procedures
For dental practices focused on cosmetic and restorative procedures like teeth whitening and veneers, cameras serve as an invaluable marketing tool. They allow dentists to objectively demonstrate treatment goals by comparing pre- and post-treatment photos of past patients’ smiles.
When recommending aesthetic treatments, dentists can instantly pull up before and after shots to illustrate exactly what can be achieved. During whitening or veneer try-in appointments, cameras document the expected results so patients can compare options until they choose the look they prefer. Afterwards, progress photos show patients and referrers the final results achieved.
These image galleries prove the transformative capabilities of various cosmetic treatments to prospective patients. Seeing real transformation stories convinces more people to invest in their smiles’ appearance and confidence. Camera evidence also builds credibility that practices can deliver natural-looking, long-lasting aesthetic outcomes worth the investment. Combined with social media sharing, dental cameras become a powerful marketing differentiator for forward-thinking practices.
The Future of Dental Imaging
While already an essential tool, dental cameras continue evolving alongside new technologies. Some future additions may include:
– 3D and intraoral scans – Cameras can capture highly detailed 3D images inside the mouth for digital model creation and restorative planning.
– Augmented reality – Enables overlaying of digital information onto live camera views to “label” features and demonstrate proposed treatments in real-time.
– Artificial intelligence – Machine learning algorithms may help analyze camera images to screen for hard to detect oral abnormalities or accurately track treatment progress.
– Teledentistry – Equipping cameras for live remote consults and diagnosis via telehealth could expand access in underserved areas.
*Note:
1. Source: Coherent Market Insights, Public sources, Desk research
2. We have leveraged AI tools to mine information and compile it