Introduction to Compounding
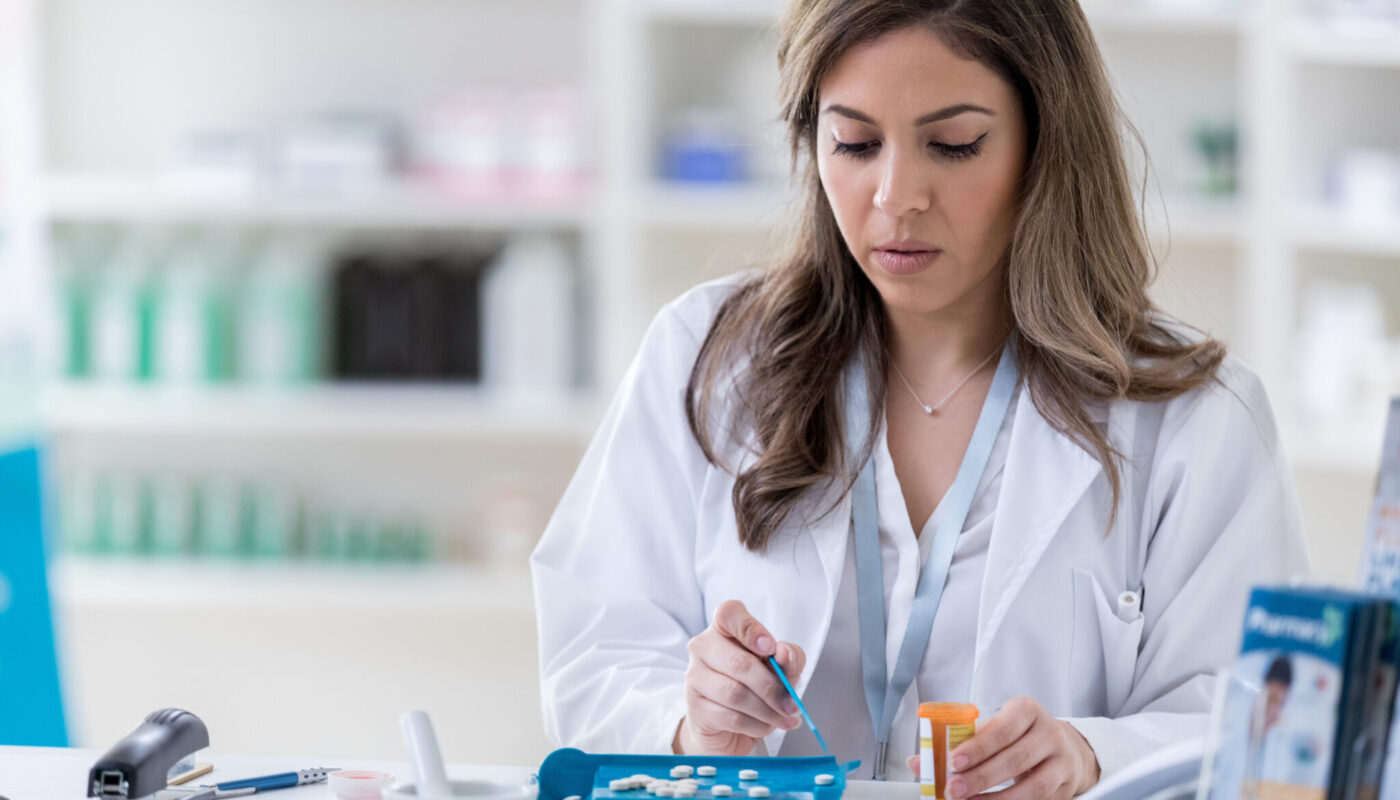
Compounding pharmacies play an important role in the healthcare industry by creating customized medication preparations based on individual patient needs. Compounding typically involves combining, mixing, or altering ingredients to create a medication tailored to a specific patient’s medical requirements. Through compounding, pharmacists are able to develop formulations not commercially available to help patients receive treatment.
The compounding process begins when a medical practitioner determines that an FDA-approved medication is not suitable for a patient due to certain factors like allergies, inability to swallow pills, or the need for an alternate dose or delivery method. The practitioner then issues a prescription for a compounded medication to be prepared by a compounding pharmacy.
History of Compounding
The art of compounding medications dates back thousands of years to ancient times when herbalists and alchemists first developed formulations by combining various plant and mineral substances. However, modern compounding pharmacy practices emerged in the 19th century. As more standardized prescription medications became available, compounding declined but was still utilized when commercially prepared drugs did not meet patient needs. In the 20th century, compounding resurged due to technological innovations and an aging population requiring more customized care. Today, compounding pharmacies remain an important niche in the larger pharmaceutical industry.
Regulations for Compounding Pharmacies
In the United States, Compounding Pharmacies are overseen by both state boards of pharmacy and the federal Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Compounders must adhere to quality standards, product testing requirements, and labeling guidelines set forth by these regulatory bodies. Clean rooms, proper equipment, and strict procedures are essential to ensure compounded medications are accurately dosed, sterile if required, and produced safely.
The FDA only regulates compounding activities that constitute manufacturing, which involves mass production and copying of commercially available products. However, the FDA has jurisdiction over compounded pharmaceutical products when contamination or other issues occur. State boards of pharmacy license compounding pharmacies and inspect facilities to ensure adherence to regulations designed to protect public health. Oversight helps guarantee compounded medications meet appropriate standards of safety, identity, strength, quality, and purity.
Types of Compounding Services
Within the scope of their training and licensing, compounding pharmacists can create a wide range of formulations tailored to individual patient circumstances through various processes:
-Capsule or tablet making combines and presses powder ingredients into final solid dosage forms.
-Creams and ointments compound semi-solid dosage forms for topical administration.
-Suppositories prepare medications for insertion into body cavities.
-Liquid medications involve suspending or dissolving ingredients in water, alcohol, oils, or other solvents.
-Troches are dissolvable lozenges used to deliver medication.
-Implants, pellets and microspheres develop specialized controlled-release formulations.
With compounds ranging from simple dose modifications to complex chemotherapeutic treatments, compounding pharmacies fulfill an important niche in healthcare delivery.
Serving Unique Patient Populations
Certain patient populations have particularly benefited from customized medications provided through compounding pharmacies:
-Pediatric patients: Compounded liquid and chewable medications have addressed the difficulty in administering commercial drugs to children.
-Geriatric patients: Seniors may have trouble swallowing pills, necessitating alternative forms like topical gels or transdermal patches.
-Patients with allergies or sensitivities: Compounding allows avoidance of dyes, preservatives, or allergenic inactive ingredients in commercial products.
-Veterinary medicine: Customized medications are essential for animal patients that cannot swallow tablets or need specific formulations and doses.
-Reproductive health: Compounded hormone therapies provide an alternative to standardized oral contraceptives or menopausal treatments.
By addressing formulation challenges and complex medical requirements, compounding pharmacies fill critical niches in patient care. Their unique services enhance healthcare access for diverse populations.
Quality Assurance in Compounding
Delivering safe, accurate medications demands stringent quality assurance processes within compounding pharmacies. Facilities take proactive steps such as:
-Implementing validation protocols to ensure recipes and procedures consistently yield the intended product.
-Adopting aseptic technique training, cleanroom certification, and microbial screening programs.
-Conducting pre-and post-production testing of compounded preparations to confirm identities, strengths, and sterility.
-Maintaining complete documentation of materials, expiration dates, batch records, and recall procedures through integrated inventory and labeling systems.
-Participating in third-party auditing and accreditation programs.
Strict adherence to standards helps compounding pharmacies earn the confidence of healthcare providers and patients that customized medications are produced under controlled conditions delivering the expected therapeutic outcomes.
The Future of Compounding Pharmacies
As individualized care rises in priority and specialized formulations grow in demand, compounding pharmacies are well-positioned to play an even greater role in tomorrow’s healthcare system. Technological advances may expand their capabilities to address more challenging compounding needs. Precision medications tailored at the molecular level could emerge. Compounding’s contribution to unmet patient needs will likely define its future development and cement its permanence within the pharmaceutics profession. Collaborations with researchers may also lead to new standardized products originating from successful compounded therapies. With adherence to regulations and focus on quality, compounding pharmacies ensure patients receive treatments catered precisely to their circumstances.
*Note:
1. Source: Coherent Market Insights, Public sources, Desk research
2. We have leveraged AI tools to mine information and compile it.