A recent study conducted by researchers at SINTEF Ocean has revealed alarming levels of toxicity in standard plastic products. The study aimed to investigate the impact of chemical additives in plastics on marine organisms, as well as potential harm to humans.
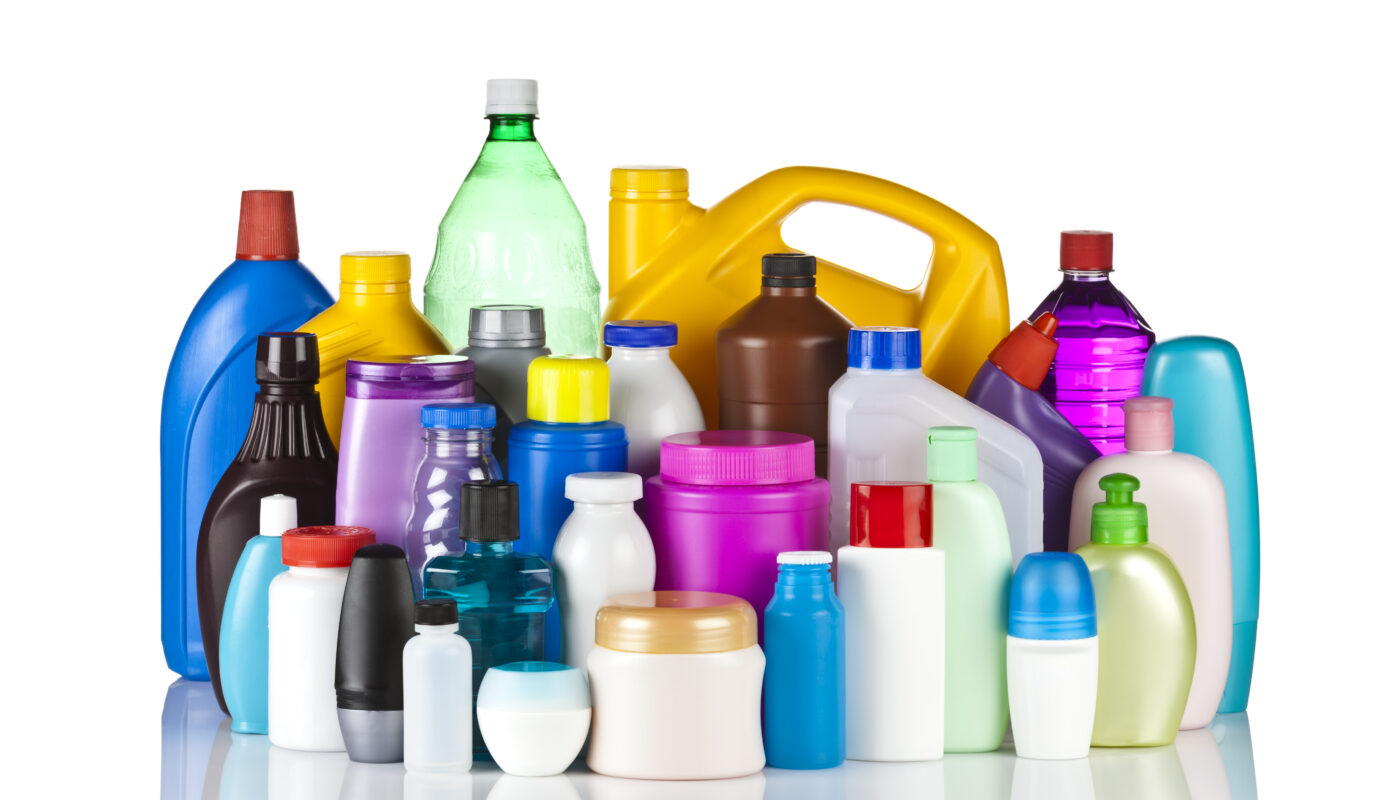
The researchers focused on a variety of marine species, including bacteria, microalgae, and the eggs and larvae of cod. They selected 50 commonly used plastic products for analysis, such as plastic bags, disposable cups, and children’s toys. Surprisingly, the team identified a wide range of different chemicals in these products, with only 30% of the chemical compounds found in two or more items. Many chemicals could not be identified as they were not listed in substance indexes.
The study aimed to assess the toxicity of these chemicals to living organisms once the plastic products enter the marine environment. The researchers found that products containing high levels of rubber had the most significant impact on microorganisms. Chemicals leaching from rubber gloves were found to be the most toxic to the microorganisms tested. Other products, such as dishwashing gloves, car tires, rubber balloons, and disposable gloves, also contained toxic substances.
Further experiments involved exposing cod embryos and larvae to microplastic particles and the identified chemicals. The researchers observed that some chemicals prevented eggs from hatching, while others caused physical deformities, similar to scoliosis, in the larvae. Surprisingly, the team found that the chemicals were essential in producing the toxic effect, and physical particles without chemicals showed no toxicity.
The study concluded that the combination of different plastic products determines the level of toxicity. Elastic plastic products, in particular, were found to be among the most toxic. The researchers suggested that toxicity could be reduced by selecting alternative polymer combinations during manufacturing.
Regarding the potential impact on food animals, the researchers stated that humans and other animals are continuously exposed to plastic-related chemical additives through macro- and microplastics. However, more research is needed to determine the extent to which these chemicals are derived from food products versus packaging.
The researchers emphasized the importance of reducing plastic use, particularly in non-essential contexts such as textiles and product overpackaging. While plastics have beneficial uses in areas like medicine and packaging, consumers should aim to avoid unnecessary plastic consumption and influence the market by choosing alternative products.
The study provides valuable insights into the levels of toxicity in standard plastic products and highlights the need for further research on the potential effects on both marine organisms and human health. The findings underscore the importance of reducing plastic waste and considering alternative materials to minimize environmental and health risks.