Introduction to Colonoscopy
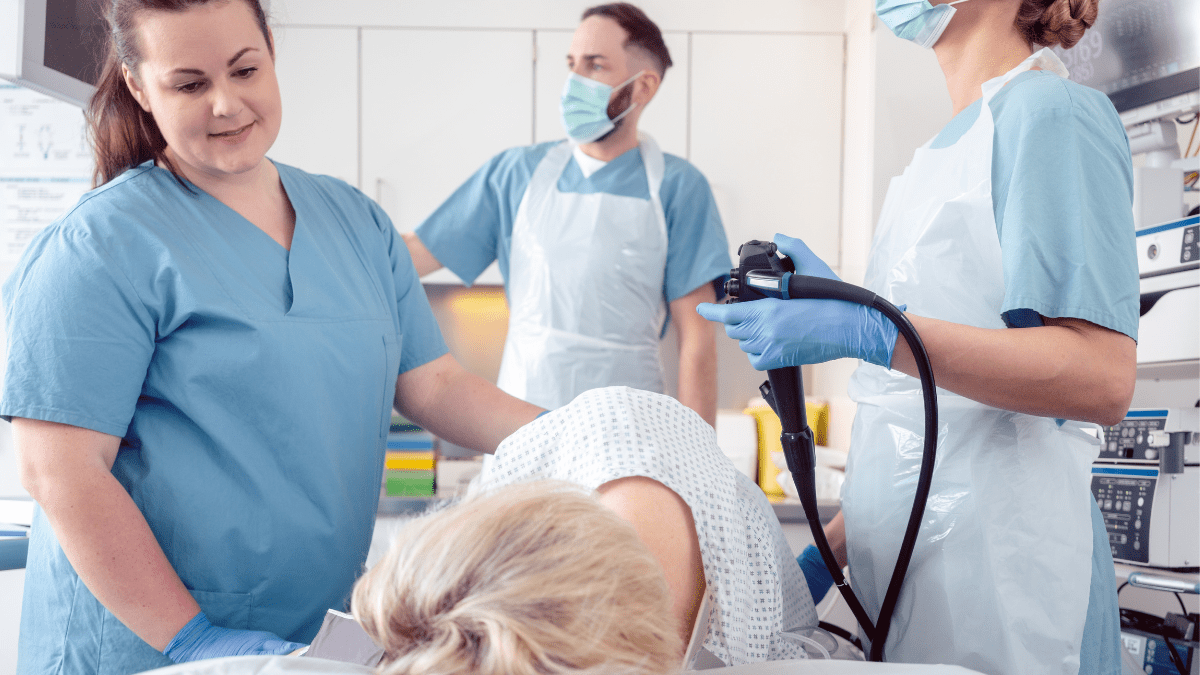
Colonoscopy is a medical procedure used to examine the inner surface of the colon and rectum. During a colonoscopy, a flexible tube called a colonoscope is inserted into the anus and guided through the entire large intestine to check for abnormalities like cancerous or precancerous polyps. Specialized tools can even be passed through the colonoscope to perform biopsies or remove polyps. Colonoscopy allows for direct visualization of the colon which is the most effective method for colon cancer screening and detection of abnormalities.
Colonoscopy Devices and Equipment
Modern colonoscopy requires specialized medical devices and equipment to perform the procedure effectively and safely. Here are some of the key devices used:
Colonoscopes
The colonoscope is the central piece of equipment used during a colonoscopy. Colonoscopes are long, thin, flexible tubes ranging from 5mm to 12mm in diameter with a video camera and light source at the tip. This allows doctors to navigate and visualize the entire length of the colon. Advancements have led to thinner colonoscopes that are more comfortable for patients and provide better image quality. Some new colonoscopes also feature articulating tips that can maneuver sharp turns better.
Insufflators
Insufflators are devices used to pump carbon dioxide gas into the colon through the colonoscope. This expands the colon and helps the colonoscope glide through easier for better views. Computerized insufflators can control gas pressure more accurately. Some new models feature carbon dioxide recirculation which reduces gas waste.
Medical Imaging Systems
State-of-the-art medical imaging systems are vital components of modern colonoscopy units. High definition cameras on the colonoscopes are linked to video processors and medical grade LCD monitors in the endoscopy room. This allows doctors and staff to have a clear, magnified view of the colon interior on a large display screen during the procedure. Some advanced systems also integrate features like optical magnification, virtual chromoendoscopy and electronic image enhancement.
Polypectomy Systems
If polyps are detected during colonoscopy, they need to be removed to examine for cancer cells. Polypectomy systems allow biopsy or resection of polyps through the colonoscope. Basic types include snares, biopsy forceps and hot biopsy forceps. Newer devices feature water jet systems, multi-fire and full-spectrum endoscopic mucosal resection techniques for precise, safe polyp removal.
Colon Cleansing Systems
Thorough colon cleansing is essential for a high quality colonoscopy. Colon hydrotherapy systems or colonic irrigation devices help cleanse the colon through controlled flushing of water. Computerized systems precisely regulate water pressure and temperature for maximum effectiveness and patient comfort. New single-use systems have reduced the risk of cross-contamination.
Colonoscopy Accessories
Other important Colonoscopy Device accessories include biopsy valve caps that hold biopsy samples, cleaning brushes to scrub the colonoscope tip, water pumps and tubing sets. Advancements provide enhanced durability, reliability and ease of use. Disposable accessories have improved sterility. New valve designs reduce air leaks for stable insufflation.
Colonoscopy Advances Driving Innovation
Continuous innovation is helping drive further advancements in colonoscopy technology. Here are some examples:
Virtual Colonoscopy
Virtual colonoscopy or CT colonography is an alternative screening method to traditional colonoscopy. It uses computed tomography scans of the colon for a noninvasive exam. While it cannot remove polyps, it provides accurate polyp detection when combined with 3D computer reconstruction and electronic cleansing of residual stool or gas. This reduces risks for those unfit for standard colonoscopy.
Colon Capsule Endoscopy
Colon capsule endoscopy uses swallowable miniature camera capsules to visualize the entire colon from the inside without any tubes inserted. Multiple tiny cameras on the capsule transmit thousands of images as it passes naturally through the digestive tract aided by laxatives. While limited to detection only, it offers a painless option for those unable to undergo standard or virtual colonoscopy.
Narrow-band Imaging
Narrow-band imaging improves visualization of mucosal and capillary patterns in the colon during colonoscopy. It uses specific wavelengths of light to enhance subtle mucosal and vascular abnormalities, increasing detection of flat or flat elevated lesions. Combined with magnified high definition views, it may help detect even tiny precancerous polyps.
Artificial Intelligence
Early AI systems are being developed and tested to analyze the huge volumes of images generated during colonoscopy, capsule endoscopy or CT colonography procedures. AI algorithms have shown capability to automatically detect and classify polyps or lesions with a level of accuracy comparable or superior to expert endoscopists. This could help address workload issues and reduce human error or oversight in polyp detection.
Robot-assisted Colonoscopy
Robotic assistance provides another avenue to enhance colonoscopy. Robot arms can potentially navigate and manipulate the colonoscope more precisely based on pre-procedure CT images. Combined with virtual reality displays, robotic control could help beginner endoscopists learn or address difficult anatomy with less discomfort for patients. Further developments may lead to single-port robotic colonoscopy without human endoscopist involvement.
Continued innovations are improving colonoscopy technology. Thinner, smarter devices deliver better views inside the colon. New methods like virtual colonoscopy and capsule endoscopy provide additional options. Advanced features like narrow-band imaging and AI aims to increase early detection rates. Overall, advancements are enhancing colonoscopy effectiveness, patient experience and making screening more accessible to Save Lives From Colon Cancer.
*Note:
1. Source: Coherent Market Insights, Public sources, Desk research
2. We have leveraged AI tools to mine information and compile it.