Cerebral angiography is a medical imaging technique used to visualize the blood vessels in the brain and neck. It helps doctors diagnose and treat various conditions affecting the brain and its blood vessels. In this article, we will explore the technique of cerebral angiography in detail along with its applications and benefits.
What is Cerebral Angiography?
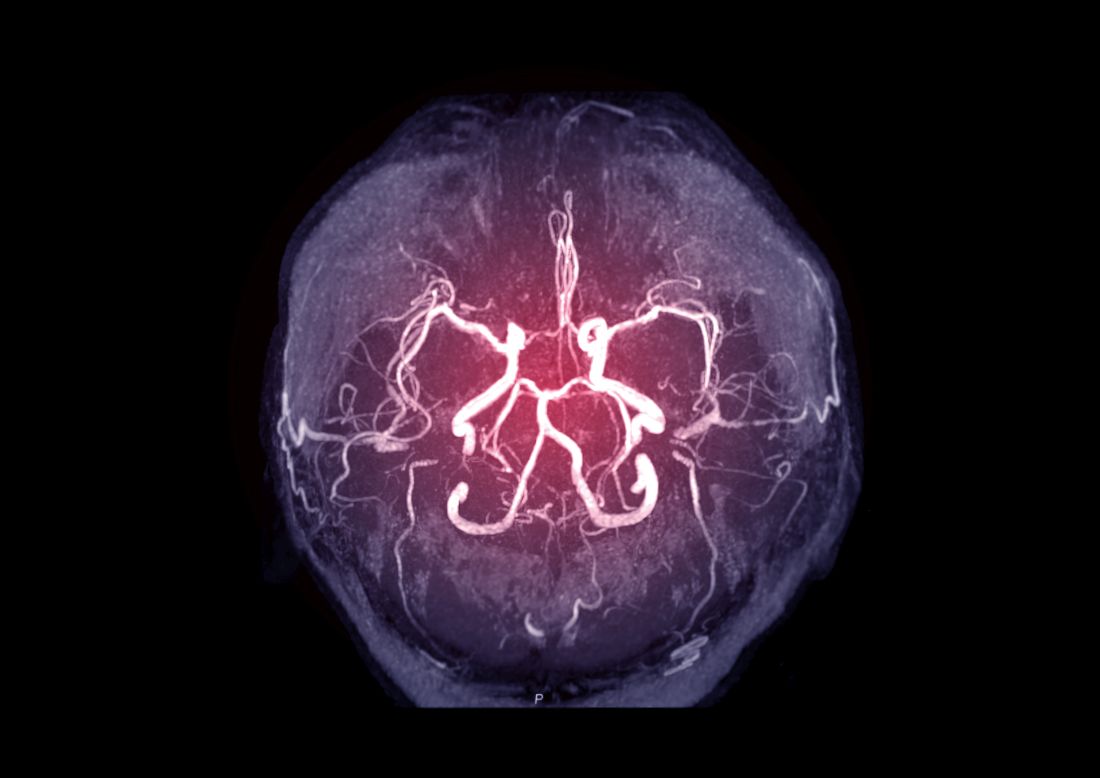
Cerebral angiography, also known as cerebral arteriography, is an invasive imaging technique where a catheter is inserted into an artery, usually in the groin area, and threaded up to blood vessels that supply the brain. Once in place, a contrast agent is injected into the catheter and X-ray images are taken. This allows radiologists to see detailed pictures of arteries and veins in and around the brain.
The main goal of Cerebral Angiography is to examine blood vessels for abnormalities such as aneurysms, blockages, arteriovenous malformations or tumors. It provides a clear view of the vascular structures that cannot be seen with other noninvasive imaging techniques. Cerebral angiography remains the gold standard for diagnosing vascular disorders of the brain.
Preparation and Procedure
Before undergoing cerebral angiography, patients are informed about risks and benefits of the procedure. Blood thinning medications may be stopped a few days prior to reduce risk of bleeding. On the day of the procedure, a local anesthetic is used to numb the groin area.
A thin catheter is then inserted into an artery in the groin and guided up to the carotid or vertebral arteries under X-ray guidance. Once in place, a contrast dye is injected through the catheter to make blood vessels visible on X-ray images. Images are rapidly taken to view blood flow and searching for any abnormalities. The procedure takes 30-90 minutes depending on complexity. Patients can usually resume normal activities the next day.
cerebral angiography is an invaluable diagnostic and interventional tool for evaluating disorders of intracranial circulation. Though invasive, it provides unmatched anatomical details about the brain’s blood vessels. Advancing technologies continue to strengthen its role by enhancing safety, efficacy and precision of treatments. With appropriate patient selection and experienced operators, it remains the gold standard investigation for many cerebrovascular conditions.
*Note:
1. Source: Coherent Market Insights, Public sources, Desk research
2. We have leveraged AI tools to mine information and compile it