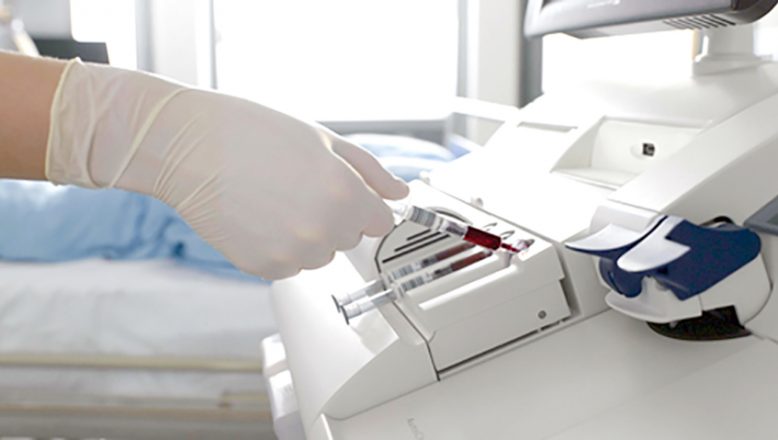
Blood gas analyzers have revolutionized how doctors diagnose and treat patients with respiratory and cardiovascular conditions. Through precise and rapid analysis of blood samples, these medical devices provide vital information about acid-base balance and oxygenation status in the body. In this article, we will explore the working, applications and importance of blood gas analyzers in modern healthcare.
What are Blood Gas Analyzers?
A blood gas analyzer is a medical device used to measure levels of oxygen, carbon dioxide, pH and electrolytes in a patient’s blood sample. The most commonly measured parameters include:
– Partial pressure of oxygen (pO2) and carbon dioxide (pCO2)
– pH (acidity/alkalinity)
– Bicarbonate (HCO3)
– Sodium (Na+) and potassium (K+)
Different models of blood gas analyzers work through electrochemical or photometric methods to analyze just 25-50 microliters of blood plasma/serum or whole blood. The analysis is completed rapidly within 2-5 minutes, providing timely diagnostic information to clinicians. Portable blood gas analyzers also exist which are small, lightweight and battery powered for point-of-care testing.
Applications in Respiratory and Cardiac Care
Blood gas tests are extremely useful for evaluating respiratory and cardiac function in patients. Analysis of blood gas parameters helps diagnose conditions affecting ventilation and oxygenation like COPD, asthma, pneumonia and pulmonary embolism. It is also valuable for monitoring treatment response in such cases.
In ICU settings, blood gas monitoring allows close tracking of a patient’s acid-base and oxygenation status, aiding management of mechanical ventilation. It is critical for patients with respiratory failure or those on supplemental oxygen therapy. Tests are also important pre and post procedures like intubation or chest tube insertion.
Any condition affecting heart function and circulation can impact blood gases as well. Tests are useful in diagnosis and management of cardiac issues like congestive heart failure, pulmonary hypertension and arrhythmias. They also help evaluate patients undergoing cardiac surgery or severely ill with conditions like sepsis and trauma.
Importance in Emergency and Critical Care
Given their rapid turnaround time, blood gas analyzers are invaluable tools in emergency and critical care areas of hospitals. They allow timely clinical decision making for acutely ill patients presenting with respiratory distress or shock. Tests can help identify life-threatening issues like hypoxemia requiring urgent oxygen supplementation or ventilation.
In trauma or cardiac arrest situations, blood gas analysis provides crucial information to guide resuscitation efforts. It indicates effectiveness of CPR, need for ventilation adjustments and guides medication administration. Serial blood gas monitoring is also important in critically ill patients admitted to ICUs for conditions like acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS).
Advantages over Conventional Testing
While pulse oximetry and respiratory monitoring are useful, blood gas analysis remains the gold standard diagnostic modality for assessing oxygenation and ventilation status. Some key advantages over regular testing include:
– Ability to directly measure pO2, pCO2 and pH levels rather than estimating them.
– Faster turnaround – results in minutes versus hours for conventional blood tests.
– Helps identify metabolic or respiratory acid-base disorders not detectable by other tests.
– More accurate evaluation of hypoxemia severity and ventilation adequacy.
– Guidance on need for oxygen therapy, NIV, intubation or other intervention.
The Future of Blood Gas Testing
As technology advances, newer generations of Blood Gas Analyzers are becoming even more portable, user-friendly and automated. Point-of-care devices are getting smaller to facilitate testing at the bedside or in ambulances. Streamlined microfluidic platforms promise lab-accurate analysis from just 1-2 μL of blood.
More parameters are also getting added to monitoring profiles. Tests for lactate, hemoglobin and electrolytes are getting integrated to provide a more comprehensive metabolic and clinical chemistry assessment. Connectivity capabilities allow real-time sharing of results with the electronic medical record for improved clinical workflow.
As critical care medicine progresses, the role of blood gas analyzers will keep expanding in specialties like cardiology, pulmonology, emergency medicine and anesthesiology. With continuous technological innovations, these devices will keep empowering doctors with faster, more actionable insights into patients’ physiologic status. Timely diagnosis and targeted therapy through blood gas analysis ultimately helps save lives on a daily basis
*Note:
1. Source: Coherent Market Insights, Public sources, Desk research
2. We have leveraged AI tools to mine information and compile it