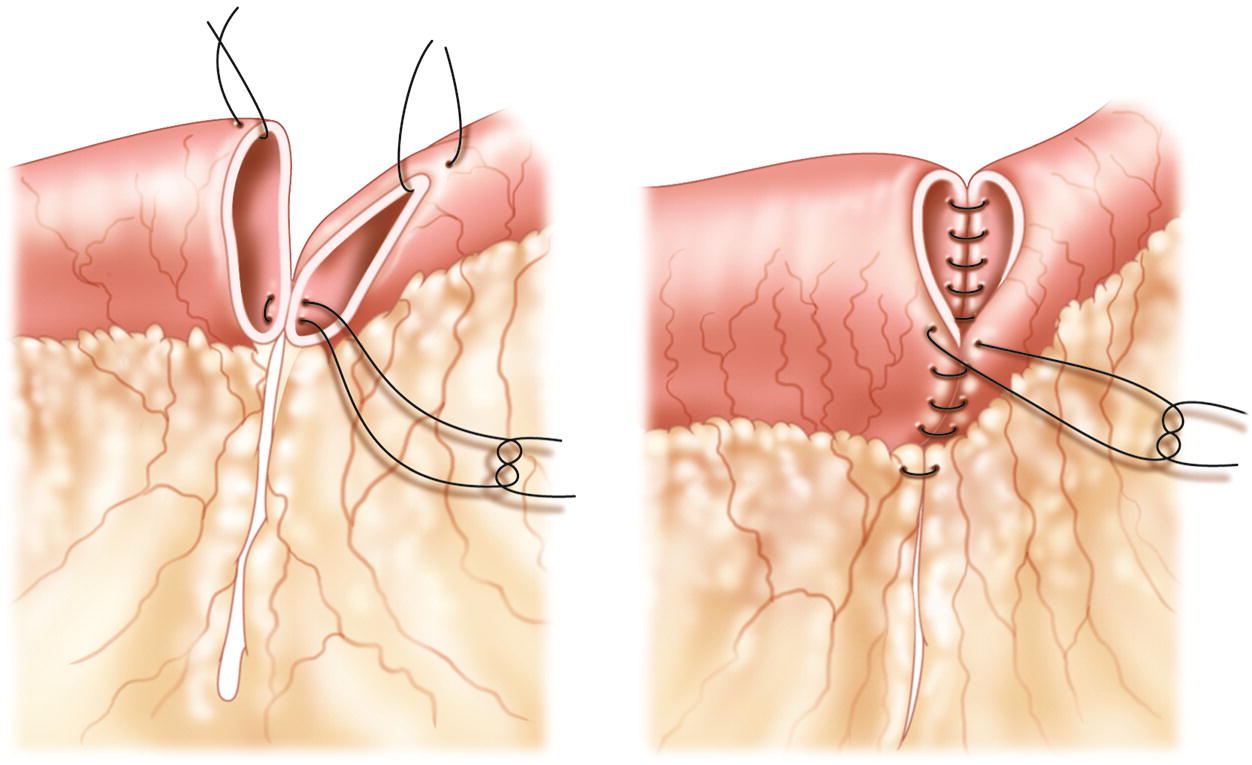
Anastomosis is commonly required after bowel resection surgeries to reconnect the severed ends of the intestines. Traditionally, anastomoses were performed manually using surgical sutures. However, in recent years various mechanical anastomosis devices have been introduced to facilitate a more precise and easier connection between tissues. These anastomosis devices aim to reduce surgical time and complications associated with manual suturing. In this article, we provide an overview of different types of anastomosis devices available and their applications.
Types of Anastomosis Devices
Stapling Devices
The most common type of anastomosis device used are surgical staplers. These stapling devices uses stainless steel staples to join the tissues instead of sutures. There are mainly two types of stapling devices – linear and circular staplers.
Linear staplers are used to perform end-to-end or side-to-side anastomoses of intestines and other tubular structures. They fire multiple parallel rows of staggered staples to seal the tissues. Linear staplers help in quicker creation of anastomoses compared to manual suturing.
Circular staplers are primarily used for lower gastrointestinal anastomoses like colorectal anastomoses. They are capable of performing end-to-end anastomoses in a single ring of tissue with one firing. This results in reduction of anastomotic leakage compared to other methods. Circular staplers have become the gold standard for colorectal anastomoses.
Non-Stapling Devices
Adhesives – Cyanoacrylate based tissue adhesives are available that can be used to seal intestinal anastomoses without use of sutures or staples. However, their long term seal strength is still not proven to be comparable to mechanical methods.
Magnetic Anastomosis Devices – These innovative devices use magnetic attraction forces to approximate and seal the tissues. External magnets are applied on skin to atraumatically join the intraluminal magnets and seal the anastomosis. However, these are still in early stages of development and need more clinical validation.
Suture-Based Devices – Devices like purse-string suturers and knot pushers help in faster placement of continuous or interrupted sutures. But they do not replace sutures completely and suturing skill is still required.
Applications of Anastomosis Devices
Colorectal Surgeries
Anastomosis devices have made colorectal surgeries safer and less invasive. Circular staplers are gold standard for low colorectal anastomosis with very low leakage rates. Even for high difficult anastomoses, staplers provide reproducibile results.
Bariatric/Weight Loss Surgeries
Sleeve gastrectomies and gastric bypasses require intestinal rearrangements which are made easy using staplers. Linear staplers help in creation of gastrojejunostomy and jejunojejunostomy with minimal trauma.
Esophageal and Gastric Surgeries
For esophagectomies or partial/total gastrectomies, use of surgical staplers lowered the anastomotic failure rates significantly compared to manual suturing. It also shortened the surgeries.
Vascular and Thoracic Surgeries
In vascular procedures like aortobifemoral bypasses or complex vascular reconstructions, use of vascular linear staplers reduce operation time and risks compared to open suturing.
Advantages of Anastomosis Devices
– Faster creation of precise, watertight Anastomoses Devices compared to manual suturing.
– Standardization and reproducibility of results between surgeries and hospitals.
– Lower training requirements compared to mastership in advanced suturing and knotting skills.
– Lower leak rates and less stricture formation at the anastomotic sites.
– Less blood loss and trauma to tissues compared to repeated insertion of suture needles.
– Shorter learning curve for surgeons to adopt stapling techniques.
– Potential for less invasive, laparoscopic procedures using endoscopic staplers.
With advancing technology, various mechanical anastomosis devices have revolutionized complex gastrointestinal and other reconstructive surgeries. Use of reliable stapling devices has enabled creation of intestinal, esophageal and vascular anastomoses with great precision and speed. This has translated to lower post-operative complications, shorter hospital stays and improved outcomes for patients. Anastomosis staplers have become an indispensable surgical tool today enabling surgeons to perform minimally invasive procedures more efficiently.
Note:
1. Source: Coherent Market Insights, Public sources, Desk research
2. We have leveraged AI tools to mine information and compile it