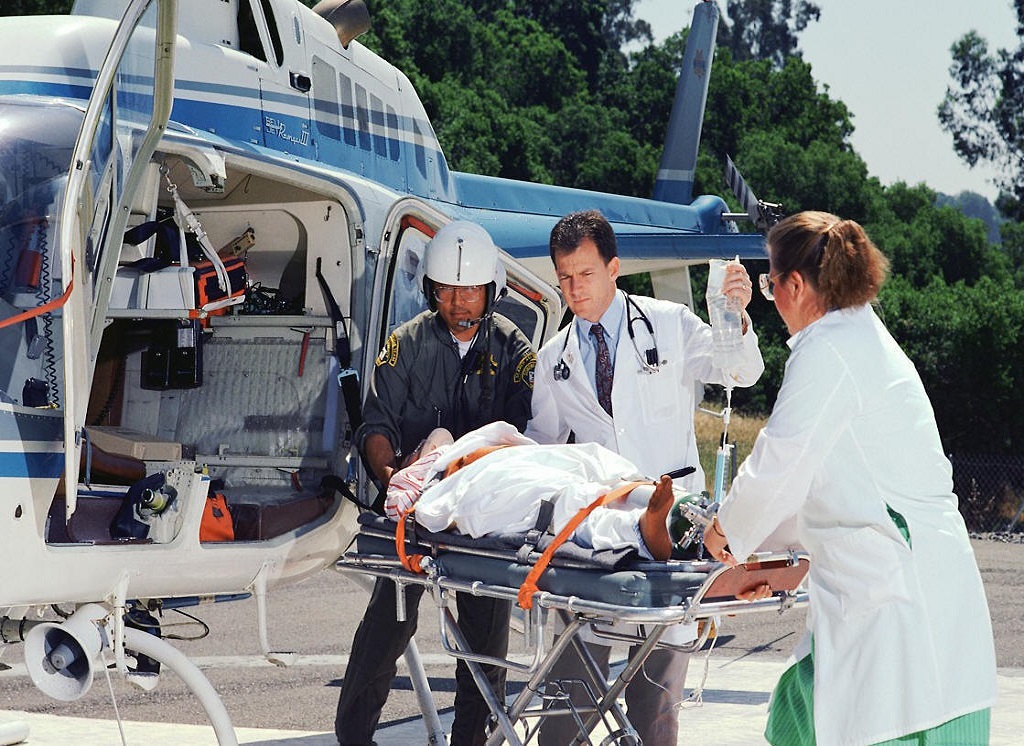
Air ambulance services have transformed emergency medical transportation. What were once considered niche aircraft primarily used for mountain search and rescue are now commonplace flying intensive care units.
A Brief History
The concept of medical air transport can be traced back to World War I when small aircraft were used to evacuate injured soldiers from remote battlefields. However, it was not until the 1950s that dedicated air ambulance services began to emerge in various parts of the world. One of the earliest was the nonprofit Air Life Line based in Washington State which provided helicopter evacuation for hikers and climbers in rugged terrain. Through the 1960s and 70s, other services started up especially in geographically diverse regions like Alaska and Australia.
The 1980s saw significant advances as helicopters were outfitted with sophisticated medical equipment turning them into mobile ICUs. Services expanded their reach and scope to transport critically ill patients between hospitals as well as from accident scenes. By the 1990s, jet aircraft were entering service to facilitate long distance transfers across states and countries. Today, advanced air ambulance services operate globally saving thousands of lives each year through rapid critical care transportation.
How Air Ambulance Services Work
Most Air Ambulance Services operate 24/7, 365 days a year on an on-call basis. They utilize helicopters and jets equipped as flying intensive care units with ventilators, IV pumps, cardiac monitors and defibrillators among other advanced life support gear. Medical teams include intensive care paramedics, nurses and sometimes even specialists like doctors and neonatologists.
When emergency calls come in, dispatch coordinates with the nearest available aircraft. Teams get enroute within minutes, even launching in dark or bad weather conditions using Night Vision Goggles or Instrument Flight Rules. At the scene, patients are quickly assessed, stabilized if needed and loaded for time-critical transport to the best receiving hospital. Enroute care continues with teams performing procedures, administering medications and addressing any changes in condition.
For inter-hospital transfers, admitting and referring physician consult to determine the right aircraft, transportation service and receiving facility based on patient acuity. Teams meet strict regulations on equipment, training and skills required to care for critically ill babies, children and adults including trauma, cardiac, stroke and neurological patients.
The Value of Air Medical Transport
Numerous research studies have demonstrated improved outcomes and survival rates associated with air ambulance transportation compared to ground ambulances in many emergency scenarios. Some of the key factors include:
Faster Transport Times – Helicopters can move faster than ground vehicles especially in congested areas or over long distances. They cut hours off transport intervals that can be critical for conditions like strokes, traumatic injuries and neonatal emergencies.
Bypasses congestion – Aircraft are not constrained by traffic allowing them to take the most direct routing possible versus winding along roads. This shaves off even more time off already time-sensitive transports.
Access to remote areas – Ground vehicles cannot reach backcountry accident sites, offshore rigs or islands but helicopters can operate anywhere including landing zones in mountains, forests and beaches to access patients.
Ability to transfer between facilities – Fly-in fly-out capability facilitates transfers between small rural hospitals and large acute care referral centers with specialists and resources beyond the local facility’s capabilities. This improves outcomes for things like burns and complex surgeries.
Continued critical care – Enroute medical teams can deliver ICU level care throughout transport including advanced procedures and lifesaving interventions not possible in an ambulance. This stabilizes patients better for arrival at the receiving hospital.
Overall, research indicates significant mortality benefits from helicopter transportation in trauma with one study showing a 19% reduction in adjusted odds of death compared to ground transport after severe injuries. Similar survival advantages have been proven for conditions like stroke, heart attacks, sepsis and neonatal emergencies where faster critical care delivery and specialist access can be life-changing.
Financing Air Ambulance Services
As demand has grown, so too have costs to operate multimillion dollar aircraft 24/7 with three person medical teams. While some programs receive government funding in places like Canada, the UK, Norway and Germany, many services in the United States are nonprofit community programs or private companies. This means substantial portions must be financed through insurance payments, memberships and fundraising.
More recently, rising bills over $40,000 per transport led some insurers to cap or deny payments leaving patients vulnerably saddled with huge airlift debts unrelated to their actual medical costs. While the 2020 No Surprises Act reined in some out-of-network charges, challenges around air ambulance coverage gaps and balancing costs with access remain. Nonprofit services work diligently on fundraising, advocacy and co-pay solutions crucial to keeping doors open during these ongoing payment debates.
The Future of Air Medical Transport
Looking ahead, advancing aviation and medical technologies promise even more life-saving applications for air ambulance services. Lighter composite airframes and more fuel efficient jet and electric aircraft will expand operational range. New navigation aids, vision systems, automatic stabilization and pilot assists aimed at all-weather access.
Telemedicine is integrating including attaching surgical experts via video to guide procedures enroute. Drones could shuttle medical cargoes or even transport defibrillators. While regulatory hurdles persist, self-flying air taxis in development may take over some rescue missions. Biometric sensors with AI will further automate real-time monitoring of vital signs.
As demand spikes from aging populations and remote working trends, air ambulance will proliferate safely moving ICUs to wherever the next patient awaits. Through dedicated professionals, advanced aeromedical systems and community support, air ambulance services are poised to transform emergency healthcare worldwide well into the 21st century. Their impact today saves lives, tomorrow promises even greater benefits through continued innovation.
*Note:
1. Source: Coherent Market Insights, Public sources, Desk research
2. We have leveraged AI tools to mine information and compile it